How Does Cryptocurrency Work: Simple Explanation for New Investors
You’ve heard about cryptocurrency. Maybe you’ve read that it’s “digital money on the blockchain.” But what does that actually mean?
Here’s the reality: most explanations either treat you like a computer science PhD or oversimplify to the point of being useless. You need something in between – a clear explanation of how cryptocurrency actually works without drowning in technical jargon.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand exactly how your money moves when you send cryptocurrency, why it’s secure, and why it doesn’t need banks to work.
The Simple Version: Cryptocurrency in 60 Seconds
Cryptocurrency works like a digital ledger that everyone can see but no one can cheat.
When you send cryptocurrency:
- You announce the transaction to a network of computers
- The computers verify you have the money to send
- They record the transaction in a permanent digital ledger
- Everyone’s copy of the ledger gets updated simultaneously
No banks. No middlemen. No single point of failure.
That’s cryptocurrency in its simplest form. Now let’s dive deeper into how this actually happens.
What Makes Cryptocurrency Different From Digital Banking
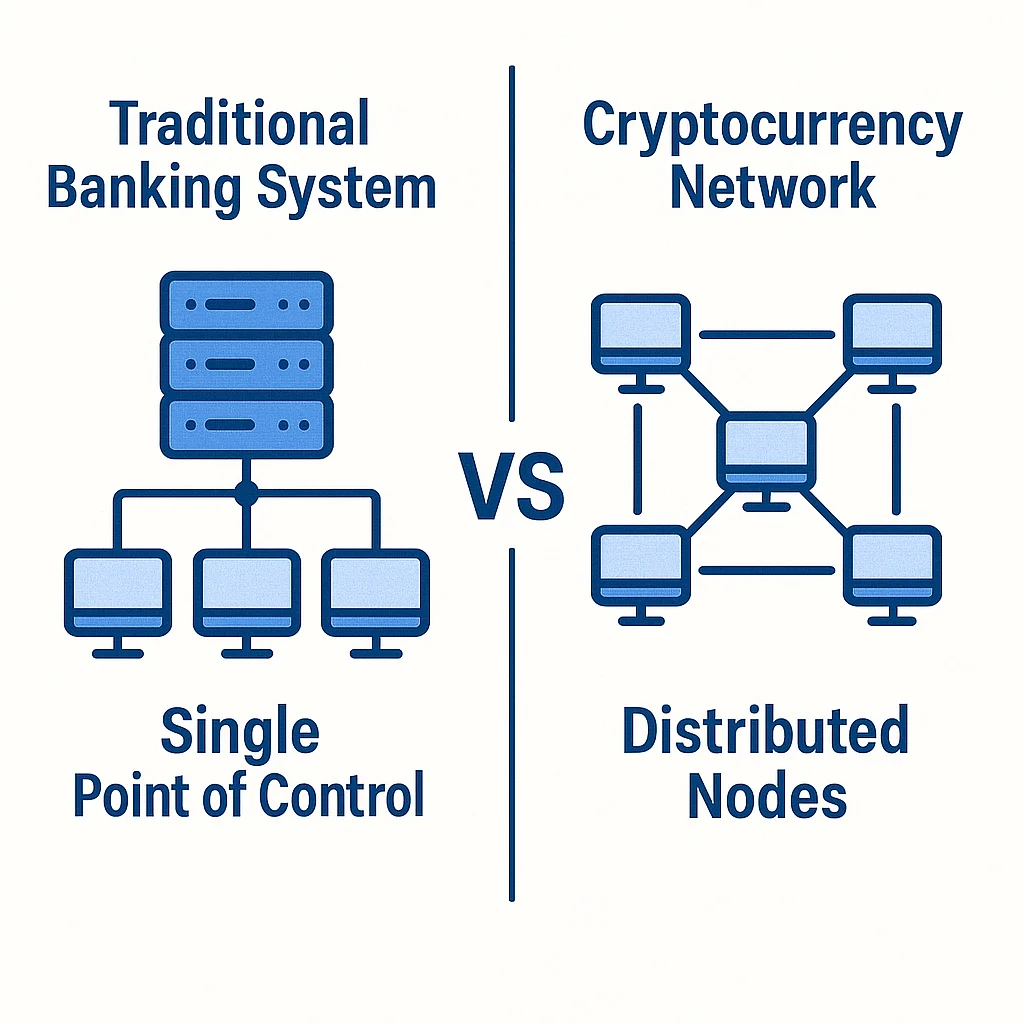
Your online banking already moves digital numbers around. So what makes cryptocurrency special?
Traditional digital money:
- Stored on your bank’s private computers
- Controlled by the bank and government regulations
- Can be frozen, reversed, or monitored
- Requires permission to access and use
Cryptocurrency:
- Stored on thousands of computers worldwide
- Controlled by mathematical rules, not institutions
- Cannot be frozen or reversed by authorities
- Requires only internet access to use
The difference isn’t just philosophical – it’s practical. [Understanding what cryptocurrency is reveals why this matters for your financial freedom.]
The Blockchain: Your Digital Ledger Explained
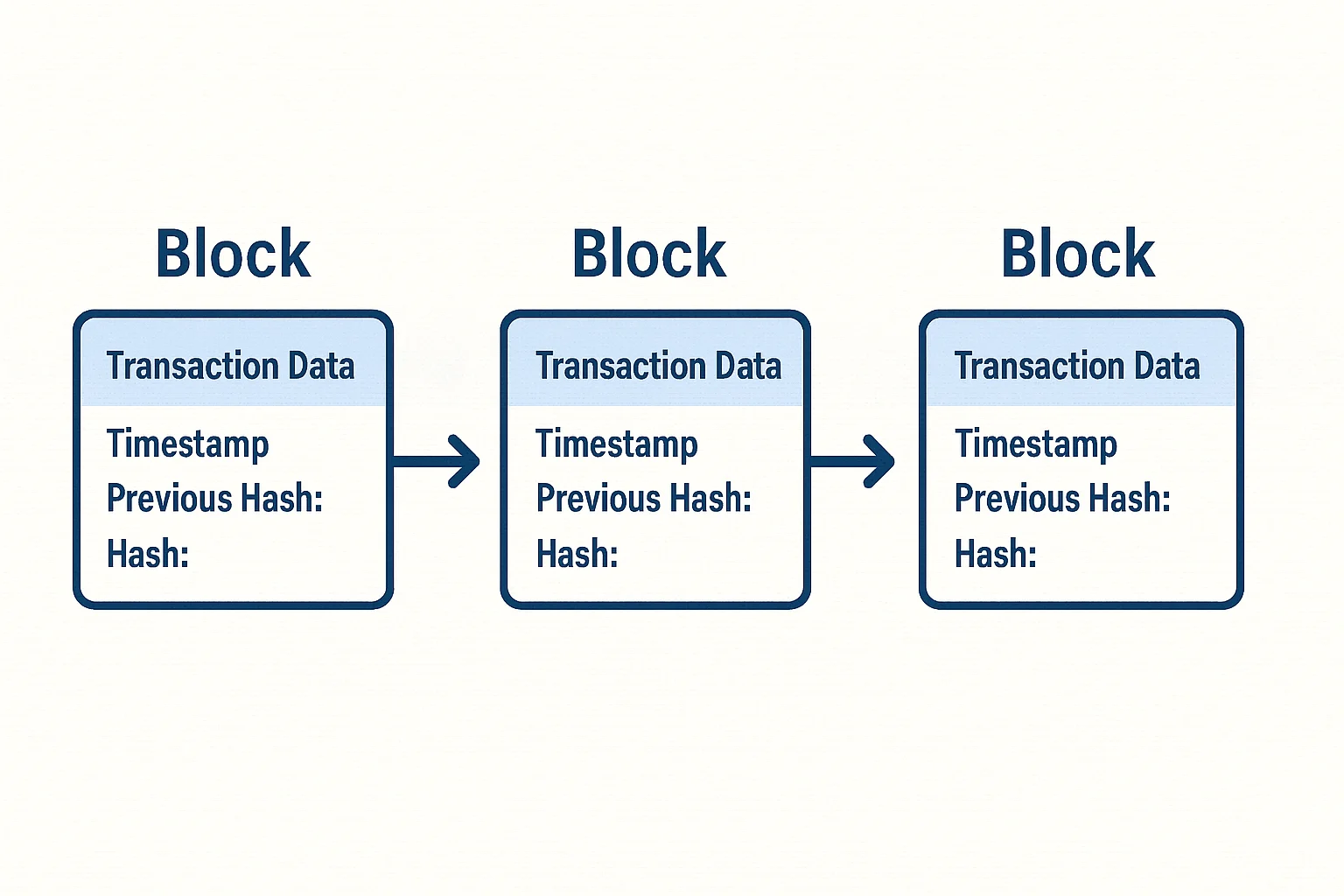
Think of blockchain as a special notebook that tracks who owns what.
But this notebook has superpowers:
It’s duplicated everywhere: Thousands of copies exist on computers worldwide It’s tamper-proof: Change one page and everyone notices It’s permanent: Once written, entries can never be erased It’s transparent: Anyone can read it, but no one controls it
How Blocks Work
Each “block” in the blockchain contains:
- Transaction records: Who sent what to whom
- Timestamp: Exactly when it happened
- Digital signature: Cryptographic proof it’s legitimate
- Link to previous block: Creates an unbreakable chain
Here’s why this matters: To fake a transaction, you’d need to simultaneously hack thousands of computers and rewrite the entire history. It’s mathematically impossible with current technology.
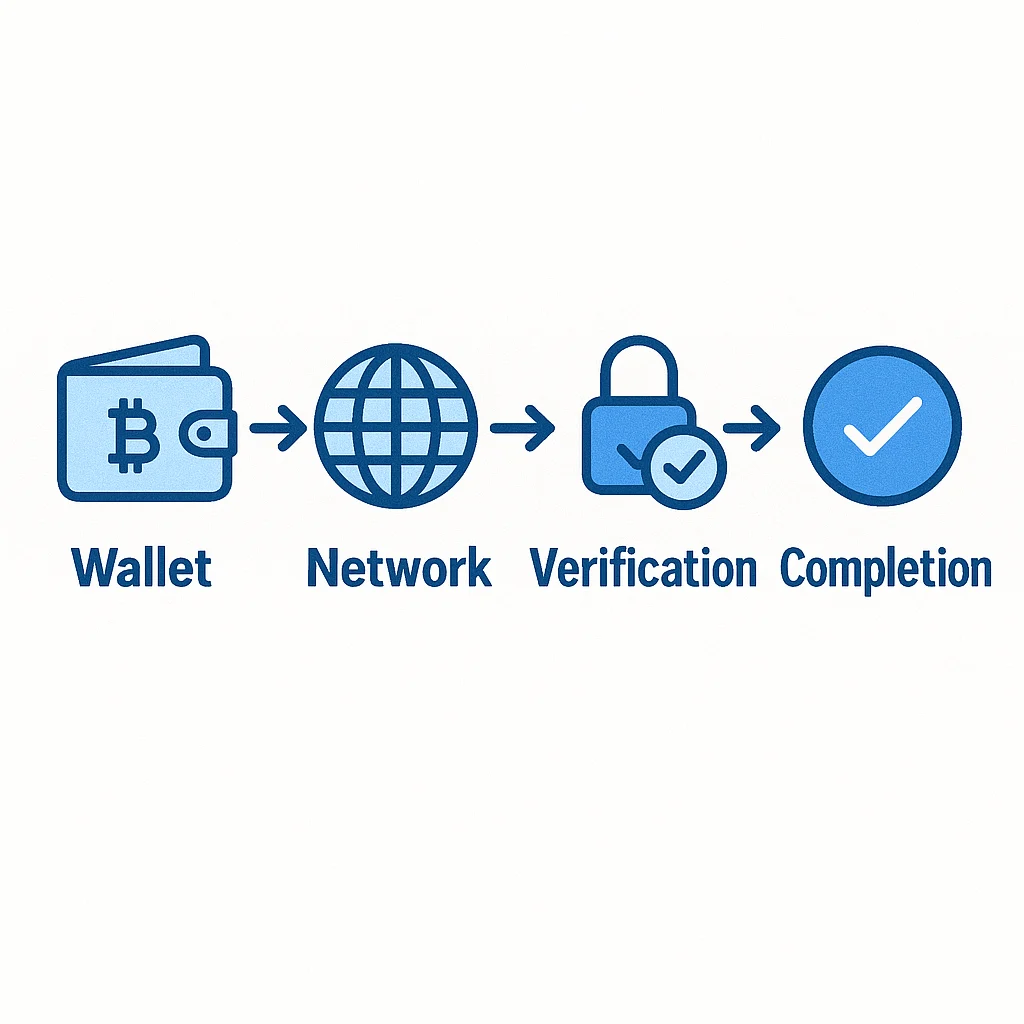
Step-by-Step: What Happens When You Send Cryptocurrency
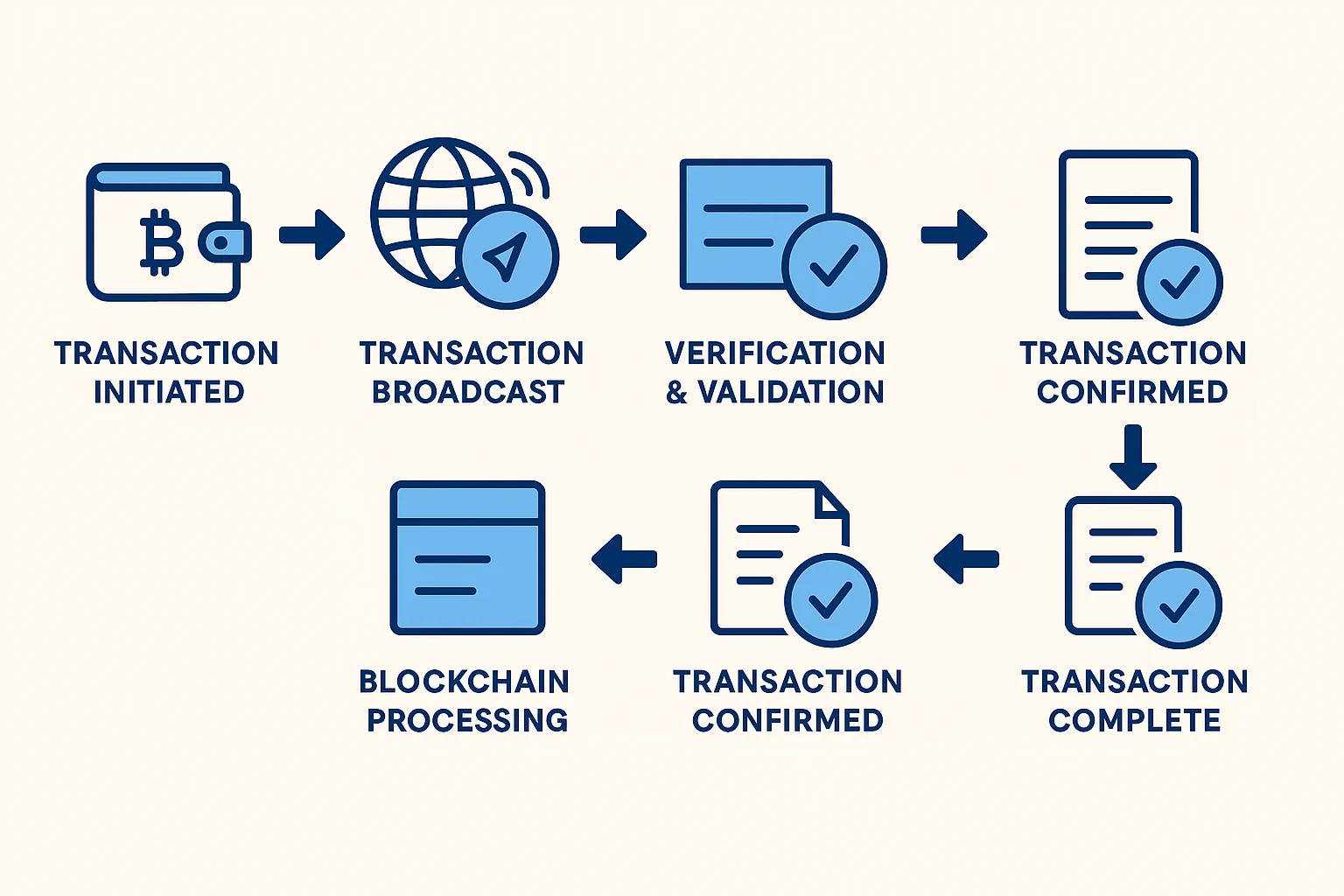
Let’s walk through exactly what happens when you send $100 worth of Bitcoin to your friend.
Step 1: You Create the Transaction
You open your cryptocurrency wallet and enter:
- Your friend’s wallet address (like a bank account number)
- The amount you want to send
- How much you’re willing to pay in fees
Your wallet creates a digital message saying “I want to send X amount to address Y.”
Step 2: Digital Signing
Your wallet “signs” the transaction using your private key – think of it as a digital signature that proves you own the cryptocurrency you’re trying to send.
This signature is unique: Only you can create it, but anyone can verify it’s real.
Step 3: Broadcasting to the Network
Your transaction gets broadcast to the cryptocurrency network – thousands of computers around the world that maintain the blockchain.
Step 4: Verification Process
Network computers (called “nodes”) check:
- Do you actually own the cryptocurrency you’re sending?
- Is your digital signature valid?
- Are you trying to spend the same money twice?
Step 5: Transaction Pooling
Valid transactions get collected into a “mempool” – essentially a waiting room for transactions about to be processed.
Step 6: Block Creation
Special network participants (miners or validators) bundle transactions from the mempool into a new block. [How cryptocurrency is created through this process is fascinating.]
Step 7: Network Consensus
The network agrees on the new block through complex mathematical processes. This prevents anyone from cheating or creating fake transactions.
Step 8: Block Addition
The new block gets added to the blockchain, and your transaction is now permanent and irreversible.
Step 9: Confirmation
Your friend’s wallet shows the received cryptocurrency. The transaction is complete.
Total time: Usually 10 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the cryptocurrency and network congestion.
Want to see this process in action? Try a small transaction on Kraken
What Are Private Keys and Public Keys?
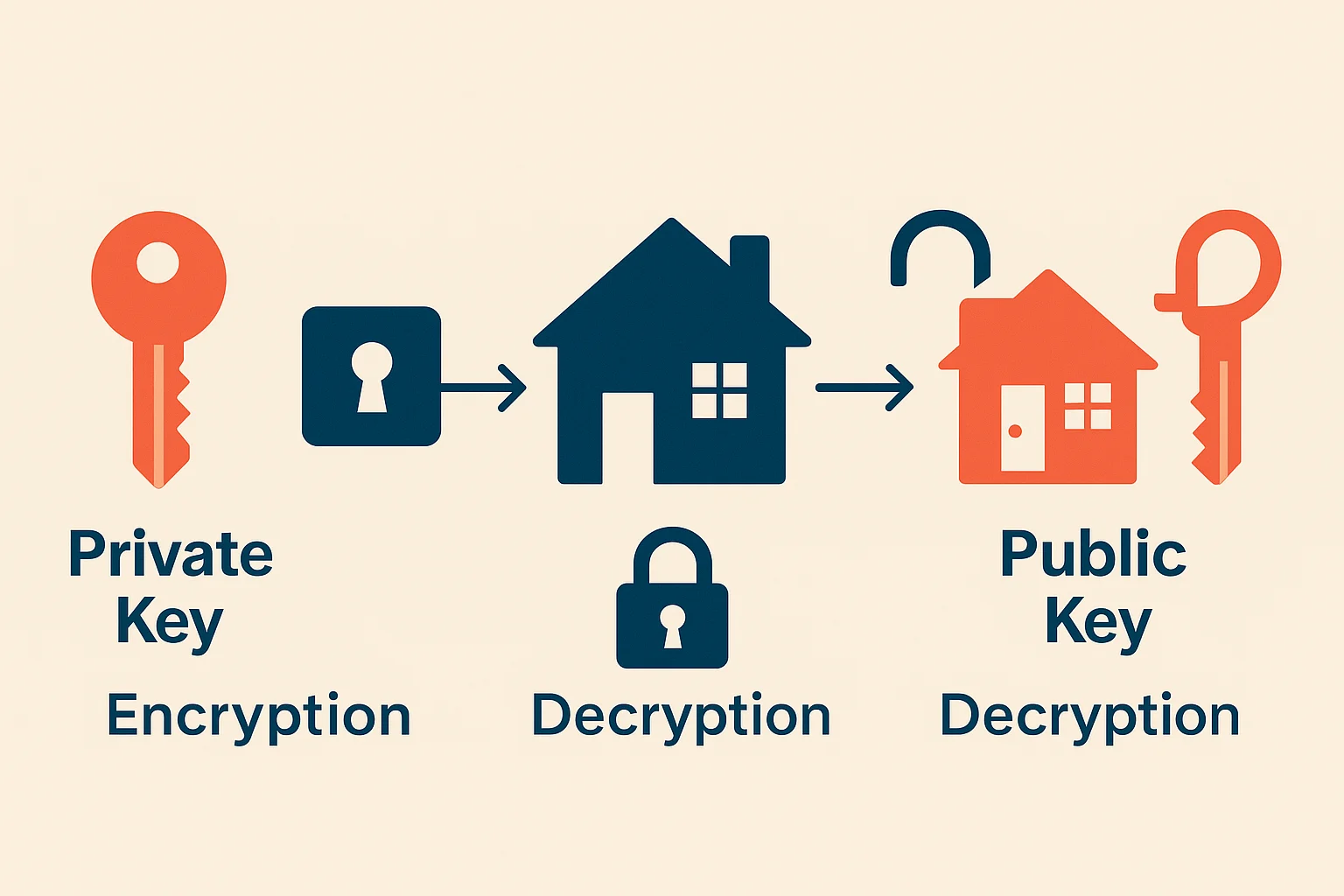
Understanding keys is crucial to understanding how cryptocurrency works.
Public Key (Your Address)
Your public key is like your home address. It’s safe to share with anyone who needs to send you cryptocurrency.
Properties:
- Generated from complex mathematics
- Safe to share publicly
- Cannot be used to steal your cryptocurrency
- Usually displayed as a long string of letters and numbers
Private Key (Your Signature)
Your private key is like the key to your house. Anyone with access to it can spend your cryptocurrency.
Properties:
- Must be kept absolutely secret
- Used to “sign” transactions and prove ownership
- Cannot be recovered if lost
- Usually displayed as a long string or as a “seed phrase”
How They Work Together
When you send cryptocurrency:
- You use your private key to sign the transaction
- The network uses your public key to verify the signature
- This proves you own the cryptocurrency without revealing your private key
Critical security point: Never share your private key with anyone. [Understanding cryptocurrency security risks is essential for protecting your investment.]
Mining vs. Staking: How Transactions Get Confirmed
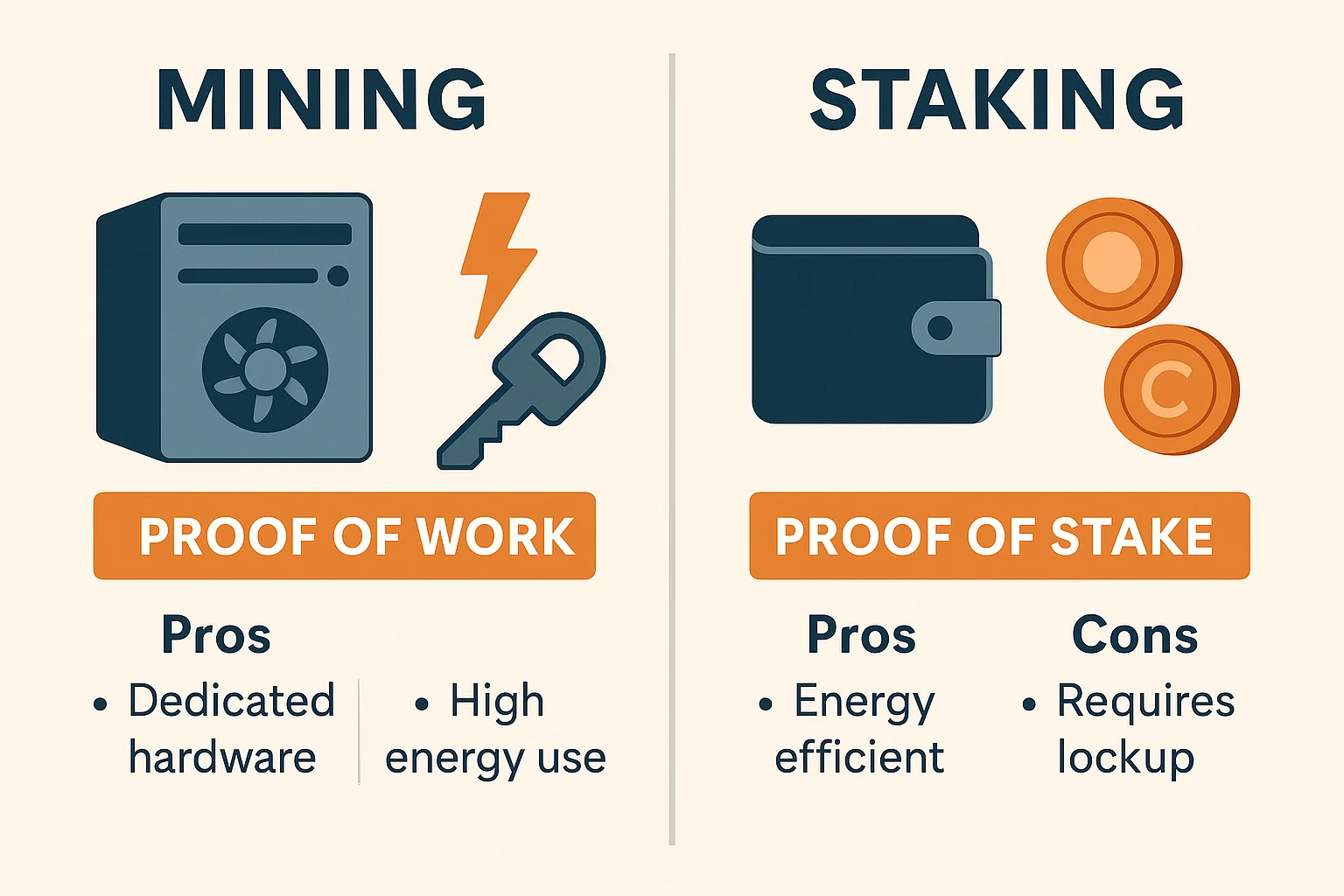
Different cryptocurrencies use different methods to confirm transactions and add them to the blockchain.
Mining (Proof of Work)
Used by: Bitcoin, Litecoin, and others
How it works:
- Computers compete to solve complex math puzzles
- First to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block
- Winner receives new cryptocurrency as a reward
- Requires significant electricity and computing power
Think of it like: A digital lottery where buying more tickets (computing power) increases your chances of winning.
Staking (Proof of Stake)
Used by: Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, and many newer cryptocurrencies
How it works:
- Users “stake” their existing cryptocurrency as collateral
- Network randomly selects validators to create new blocks
- Validators receive transaction fees as rewards
- Much more energy-efficient than mining
Think of it like: A security deposit system where having more stake gives you more chances to validate transactions and earn rewards.
Transaction Fees: Why They Exist and How They Work
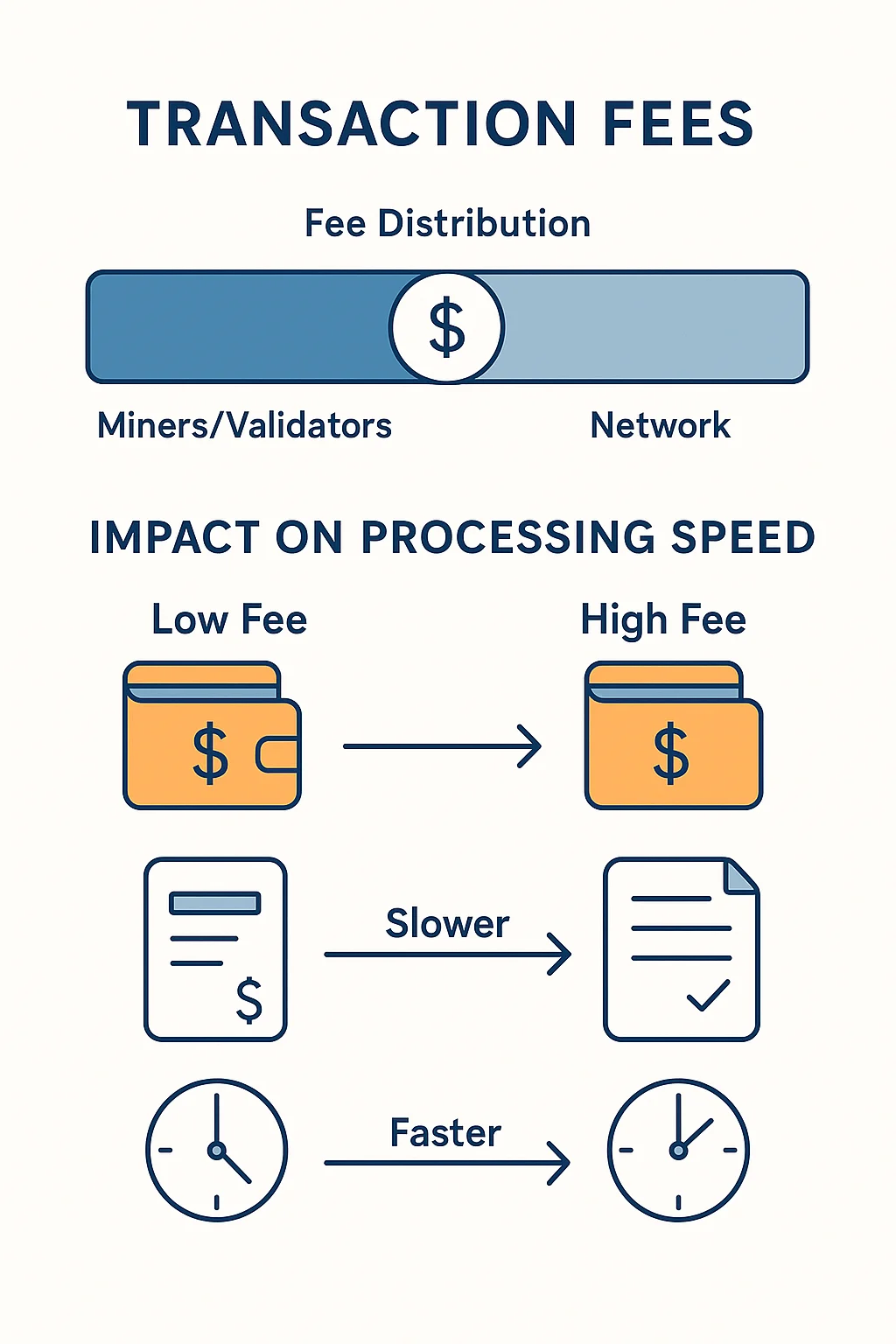
Every cryptocurrency transaction includes a fee. Here’s why and how it works.
Why Fees Exist
Network security: Fees reward miners/validators for maintaining the network Spam prevention: Fees prevent people from flooding the network with junk transactions Resource allocation: Higher fees get priority processing during busy periods
How Fees Are Calculated
Network congestion: More users = higher fees Transaction complexity: Simple transfers cost less than complex smart contracts Speed preference: Pay more to get confirmed faster
Typical fees:
- Bitcoin: $1-20 depending on network congestion
- Ethereum: $5-50+ during peak usage
- Newer cryptocurrencies: Often under $1
Fee Strategies
For regular users: Use standard fees unless you need fast confirmation For time-sensitive transactions: Pay higher fees for priority processing For large amounts: Even high fees are small compared to traditional wire transfer costs
Smart Contracts: Programmable Money
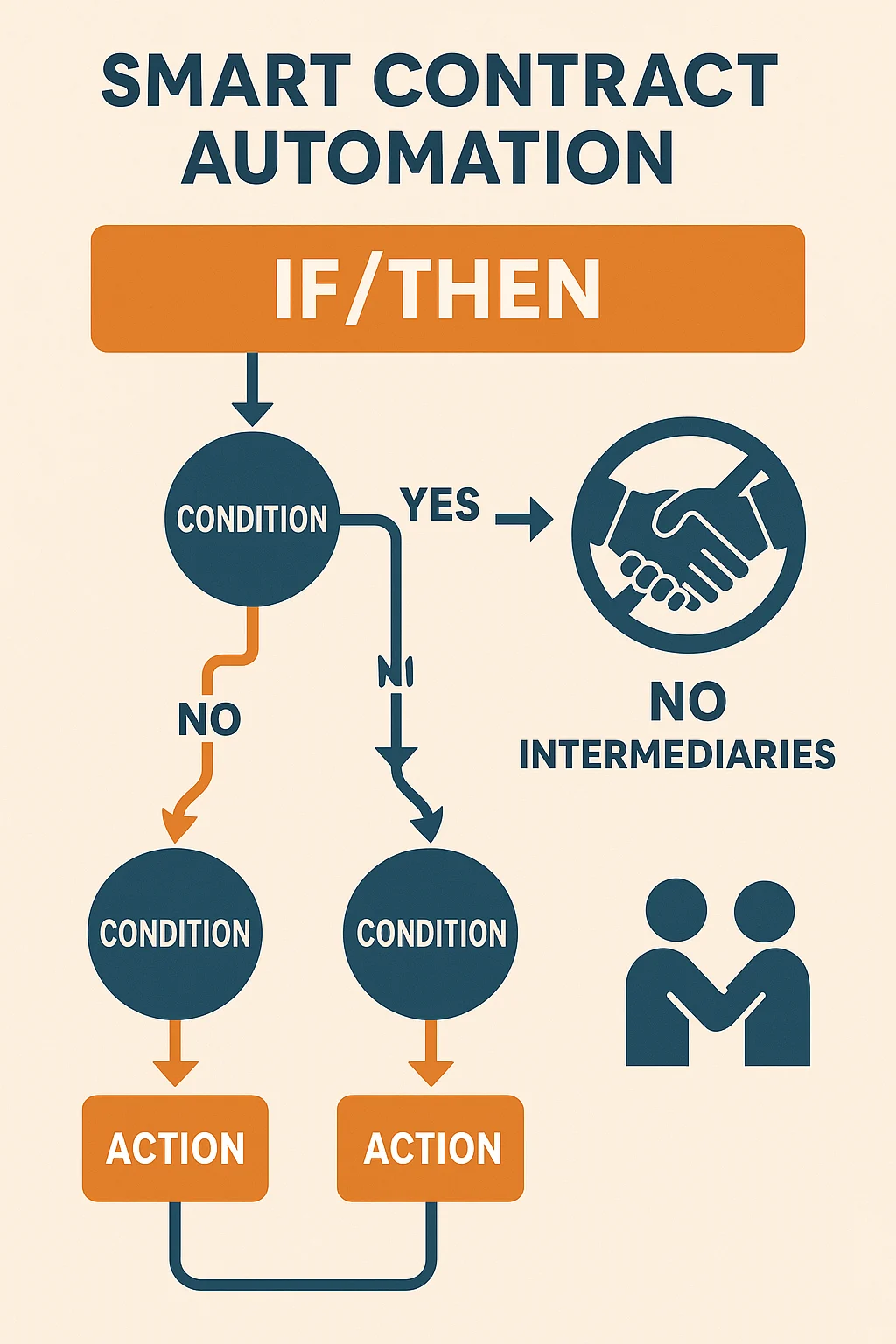
Some cryptocurrencies (like Ethereum) can do more than just transfer value – they can execute programs called “smart contracts.”
What Smart Contracts Do
Automatic execution: Contracts that run themselves when conditions are met No intermediaries: No lawyers, banks, or escrow services needed Transparent rules: Anyone can see exactly how the contract works Unstoppable: Once deployed, they run exactly as programmed
Real-World Examples
Insurance: Automatic payouts when flight delays are detected Lending: Borrow cryptocurrency with automatic collateral management Trading: Decentralized exchanges that operate without company control Gaming: In-game items you actually own and can trade freely
Why This Matters
Smart contracts enable [types of cryptocurrency applications that go far beyond simple money transfers.]
Wallet Types: Where Your Cryptocurrency Lives
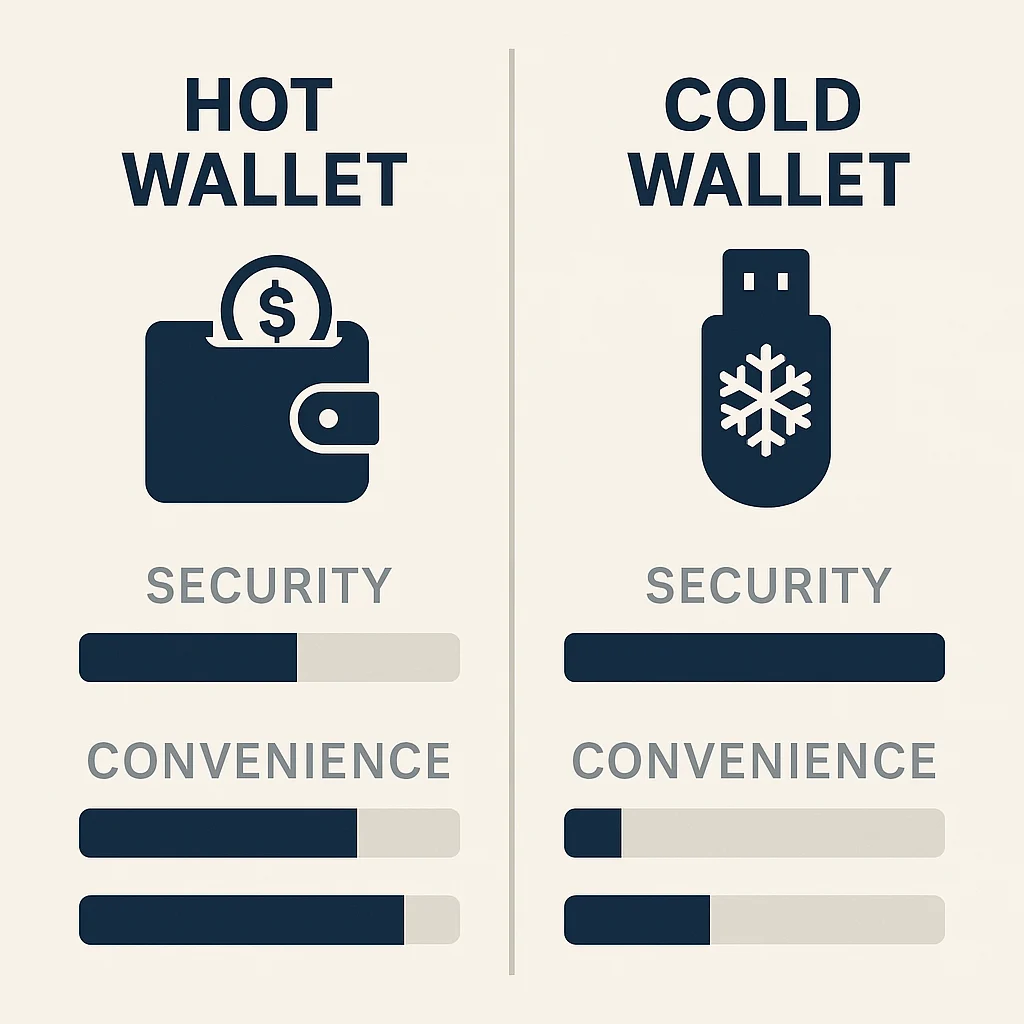
Your cryptocurrency doesn’t actually live “in” your wallet. The wallet stores your private keys that control your cryptocurrency on the blockchain.
Hot Wallets (Connected to Internet)
Examples: Mobile apps, web browsers, exchange accounts
Pros:
- Convenient for frequent transactions
- Easy to use for beginners
- Often free
Cons:
- Vulnerable to hacking
- Dependent on third-party services
- Less secure for large amounts
Cold Wallets (Offline Storage)
Examples: Hardware wallets, paper wallets
Pros:
- Maximum security
- Immune to online hacking
- You control your private keys
Cons:
- Less convenient for frequent use
- Requires initial purchase
- Responsibility for physical security
Understanding what happens when you buy cryptocurrency includes choosing the right wallet type.
Network Effects: Why More Users Make It Better
Cryptocurrency networks become more valuable and secure as more people use them.
Security Through Numbers
More nodes: More computers maintaining the network makes it harder to attack More miners/validators: Increased competition makes the network more secure More transactions: Higher activity makes attacks more expensive
Utility Through Adoption
More merchants: More places to spend cryptocurrency More developers: Better apps and services More liquidity: Easier to buy and sell without affecting prices
This creates a positive feedback loop where success breeds more success.
Common Misconceptions About How Crypto Works
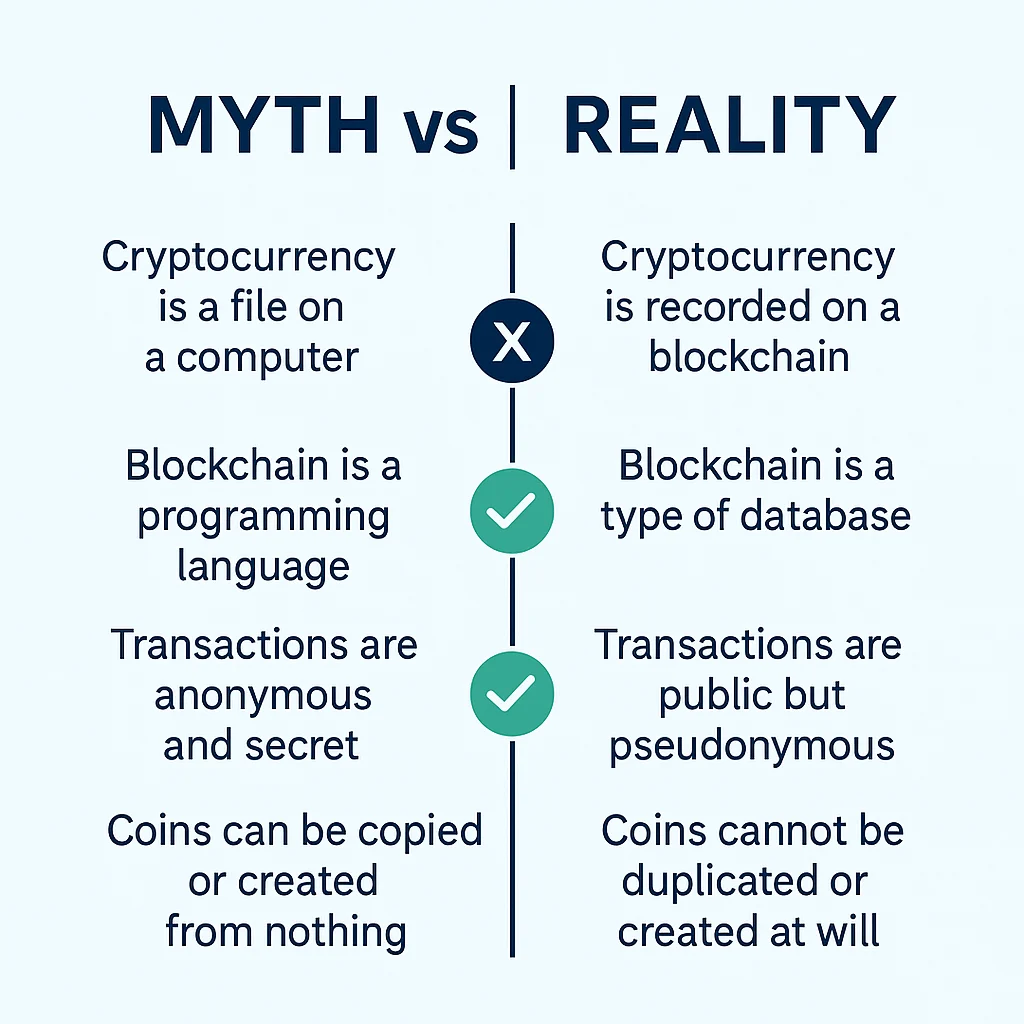
Let’s clear up some confusion about how cryptocurrency actually works.
Myth: “Cryptocurrency is anonymous” Reality: Most cryptocurrencies are pseudonymous – transactions are public but tied to addresses, not names directly.
Myth: “Transactions are instant”
Reality: Transactions appear quickly but need network confirmations for security. This takes minutes to hours.
Myth: “It’s completely untraceable” Reality: Blockchain analysis can often link transactions to real identities through various methods.
Myth: “If you lose your private key, the cryptocurrency is gone forever” Reality: This is actually true – there’s no customer service to call for cryptocurrency.
Myth: “Cryptocurrency mining wastes electricity for no reason” Reality: Mining secures the network and processes transactions – it’s the cost of decentralization.
Many cryptocurrency myths persist because people don’t understand the underlying technology.
Scalability: Handling More Transactions
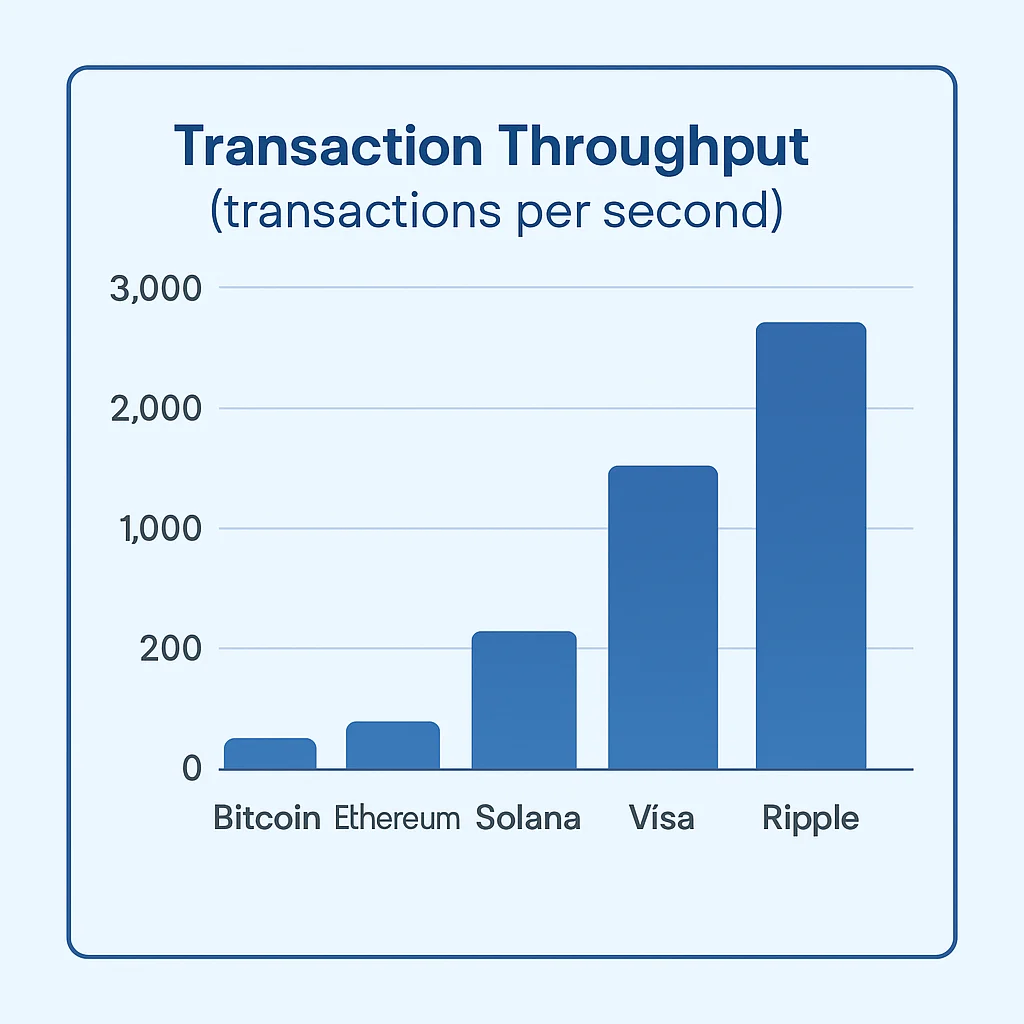
Early cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin can only process a few transactions per second. This creates challenges as adoption grows.
Current Limitations
Bitcoin: ~7 transactions per second Ethereum: ~15 transactions per second
Visa: ~65,000 transactions per second
Solutions Being Developed
Layer 2 networks: Process transactions off the main blockchain then batch them together Sharding: Split the network into smaller pieces that can process transactions in parallel Improved consensus mechanisms: Faster ways to agree on transaction validity
Why This Matters
Scalability improvements are crucial for cryptocurrency to compete with traditional money in everyday transactions.
Security: What Protects Your Cryptocurrency
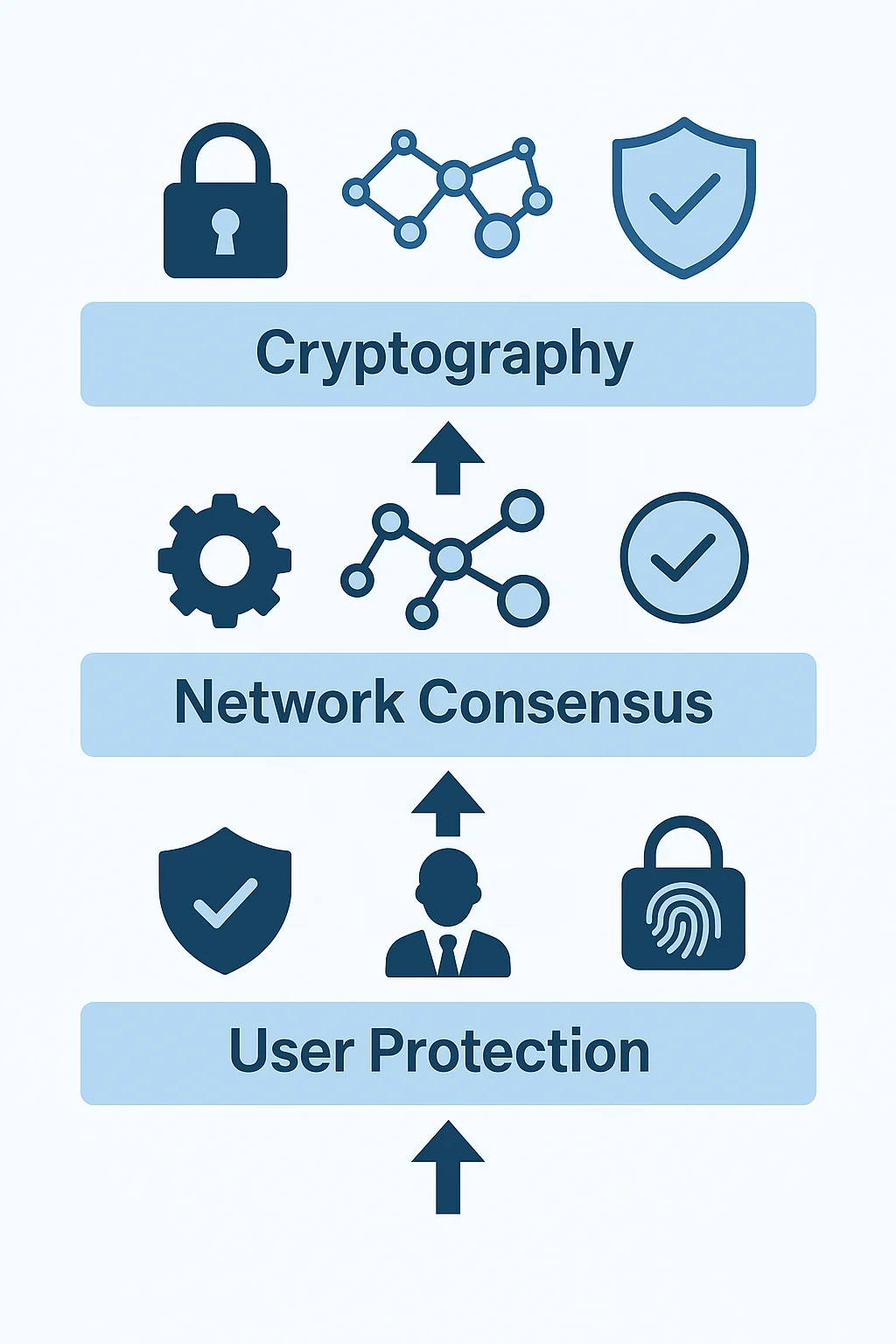
Cryptocurrency security operates at multiple levels.
Cryptographic Security
Hash functions: Turn transaction data into unique digital fingerprints Digital signatures: Prove ownership without revealing private keys
Merkle trees: Efficiently verify large amounts of data
Network Security
Decentralization: No single point of failure Consensus mechanisms: Multiple parties must agree on transaction validity Economic incentives: Attacking the network costs more than the potential rewards
Personal Security
Private key management: Keep your keys secret and backed up Hardware wallets: Store keys offline for maximum security Multi-signature: Require multiple keys to authorize transactions
Ready to upgrade to hardware wallet security? Trezor offers military-grade protection
The Role of Exchanges in Cryptocurrency
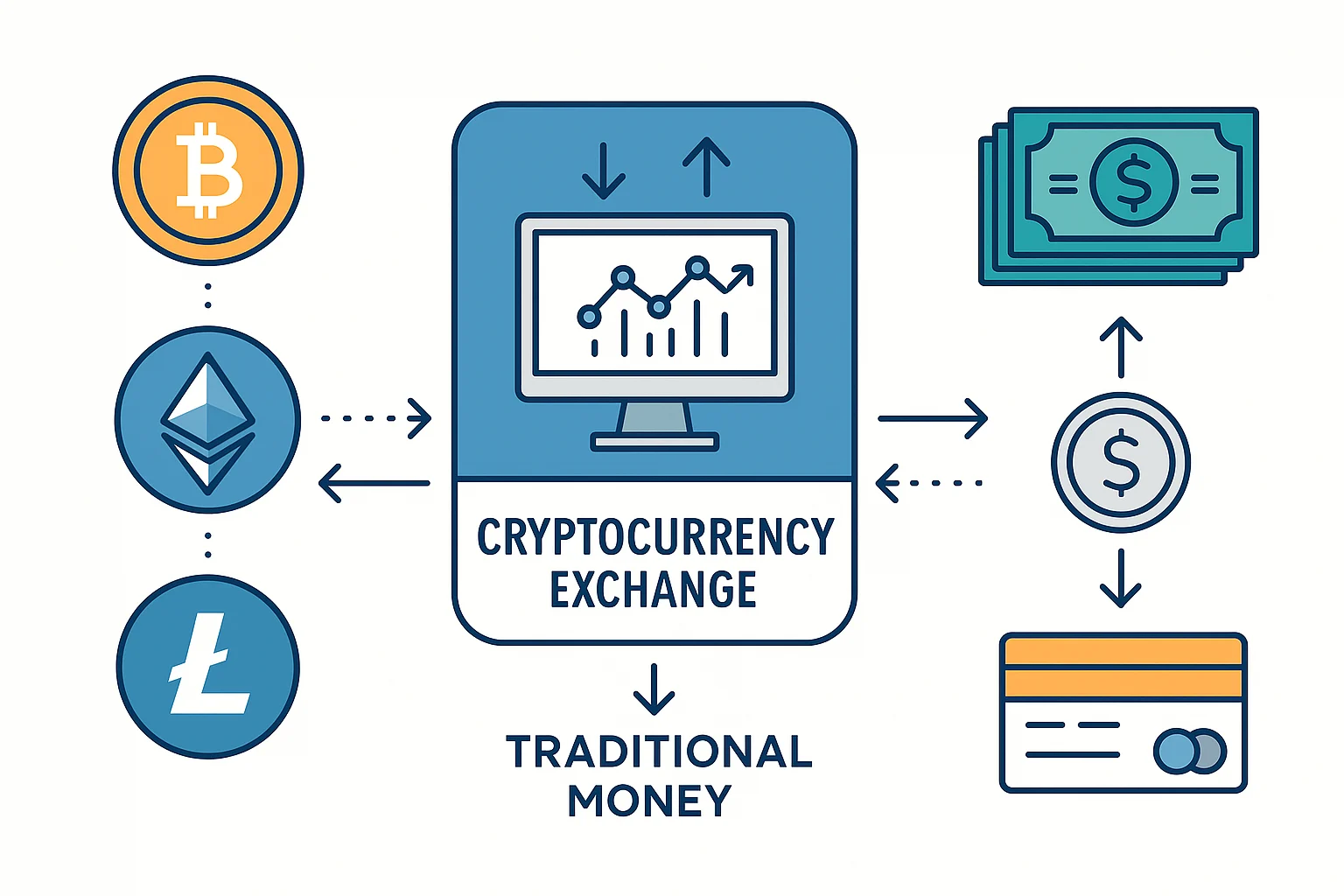
While cryptocurrency can work without intermediaries, exchanges make it practical for everyday users.
What Exchanges Do
Fiat on-ramps: Convert dollars to cryptocurrency and vice versa Trading pairs: Exchange one cryptocurrency for another Custody services: Store cryptocurrency for users who don’t want to manage private keys Liquidity: Pool buyers and sellers to enable efficient trading
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges
Centralized (Coinbase, Kraken):
- Easy to use
- Support fiat currency
- Regulated and insured
- You don’t control your private keys
Decentralized (Uniswap, SushiSwap):
- You control your private keys
- No single point of failure
- Often lower fees
- More complex to use
Finding the best cryptocurrency apps for beginners often means starting with centralized exchanges.
Future Developments: Where Cryptocurrency Is Heading
Cryptocurrency technology continues evolving rapidly.
Technical Improvements
Faster transactions: New consensus mechanisms reducing confirmation times Lower fees: Layer 2 solutions making micro-transactions practical Better privacy: Advanced cryptography protecting user data Energy efficiency: Moving away from energy-intensive mining
New Applications
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Banking services without banks Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Unique digital assets Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Government-issued digital money Internet of Things (IoT): Devices making autonomous payments
Regulatory Clarity
Legal frameworks: Clearer rules for businesses and individuals Tax guidance: Better understanding of cryptocurrency taxation Consumer protection: Safeguards for everyday users
The history of cryptocurrency shows consistent innovation and adaptation.
Key Takeaways: Understanding How Cryptocurrency Works

Cryptocurrency works through:
- Distributed networks that maintain shared transaction records
- Cryptographic security that protects against fraud and manipulation
- Consensus mechanisms that ensure all network participants agree on transaction validity
- Economic incentives that motivate people to maintain network security
The process is:
- Secure (cryptographically protected)
- Transparent (publicly verifiable)
- Decentralized (no single point of control)
- Irreversible (permanent once confirmed)
Your role is:
- Protecting your private keys
- Choosing appropriate wallet types
- Understanding transaction fees
- Following security best practices
Getting Started: Your Next Steps
Now that you understand how cryptocurrency works, here’s how to start using it safely:
Education First
Continue learning about cryptocurrency fundamentals before investing.
Start Small
Practice with small amounts while you’re learning. Understanding cryptocurrency risks helps you invest responsibly.
Choose Your Tools
Research the best cryptocurrency options for beginners before making your first purchase.
Prioritize Security
Protect your accounts with YubiKey hardware authentication.
Stay Informed
Follow the best cryptocurrency podcasts to stay updated on developments.
Take your knowledge further with Crypto Crew University’s comprehensive courses.
The Bottom Line
Understanding how cryptocurrency works isn’t just academic knowledge – it’s practical information that helps you use this technology safely and effectively.
Cryptocurrency represents a fundamental shift from trusting institutions to trusting mathematics and decentralized networks. The technology is complex, but the concept is simple: digital money that works without requiring permission from banks or governments.
Whether you’re planning to invest, use cryptocurrency for transactions, or just want to understand this growing technology, knowing how it works gives you the foundation to make informed decisions.
The future of money is being written in code. Now you understand how to read it.
This article provides educational information about cryptocurrency technology. Always do your own research and consider your risk tolerance before making investment decisions.
