Is Cryptocurrency Legal? A Beginner’s Guide to Crypto Regulations

Let’s cut through the confusion right now: Yes, cryptocurrency is legal in most developed countries.
But here’s what makes this question complicated – the legal landscape changes rapidly, varies dramatically by location, and depends heavily on what you’re actually doing with cryptocurrency.
You’re not just asking “is it legal?” You’re really asking: “Can I buy it? Can I use it? Will I get in trouble? What about taxes?”
Here’s everything you need to know about cryptocurrency legality, broken down by country, use case, and what it means for you as a beginner.
The Global Legal Status: The Big Picture
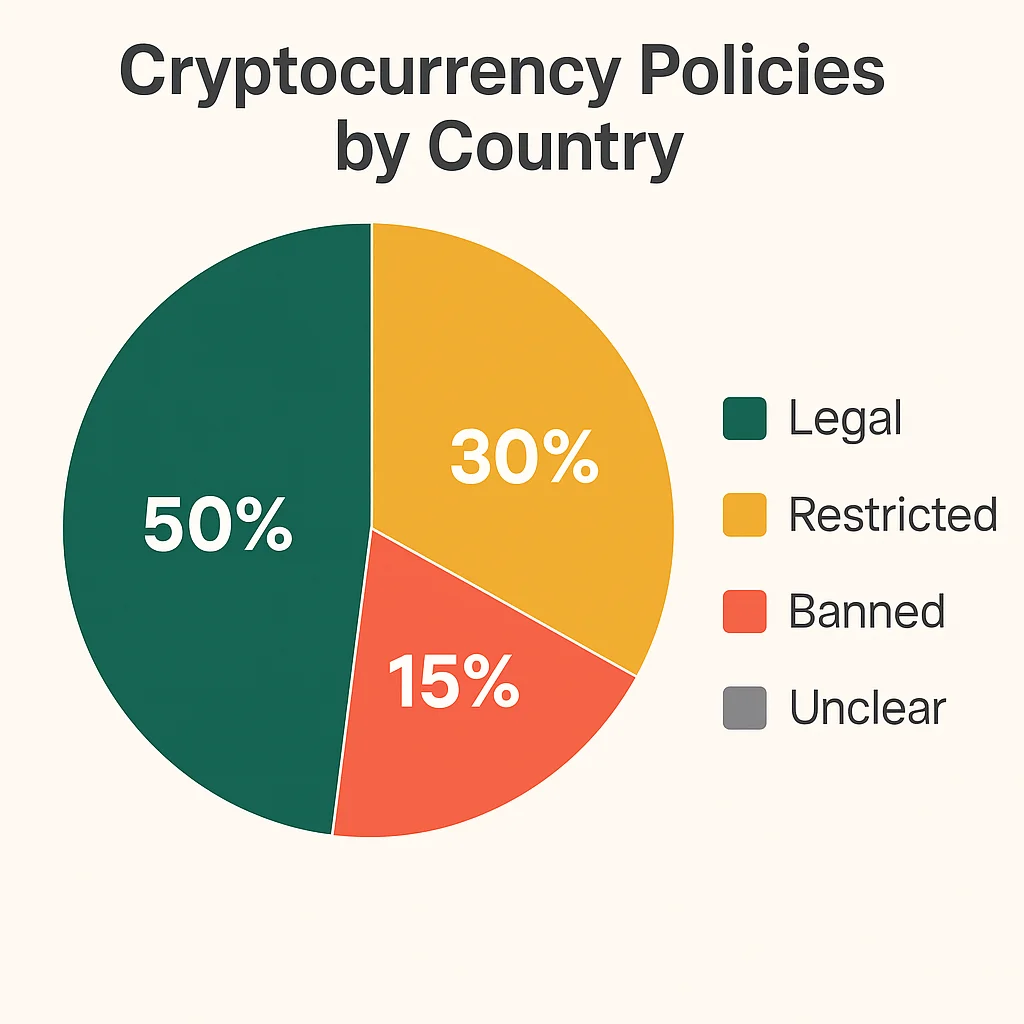
Legal and regulated: United States, Canada, European Union, Japan, Australia, Singapore Legal but limited regulation: United Kingdom, South Korea, Switzerland
Restricted or complex: India, Russia, China (mining banned, holding unclear) Banned: Bangladesh, Algeria, Egypt, Iraq, Morocco, Nepal Evolving/Unclear: Most of Africa, parts of South America and Asia
The trend is clear: Major economies are choosing regulation over prohibition. They want to control and tax cryptocurrency, not eliminate it.
Understanding what cryptocurrency actually is helps explain why governments are regulating rather than banning it.
United States: Completely Legal with Reporting Requirements

The short answer: Cryptocurrency is completely legal in the United States at the federal level.
Federal Legal Framework
IRS Treatment: Cryptocurrency is treated as property for tax purposes SEC Oversight: Some cryptocurrencies classified as securities CFTC Regulation: Bitcoin and Ethereum classified as commodities FinCEN Requirements: Exchanges must follow anti-money laundering rules
What This Means for You
✅ You can legally buy cryptocurrency
✅ You can legally sell cryptocurrency
✅ You can legally trade cryptocurrency
✅ You can legally mine cryptocurrency
✅ You can legally accept cryptocurrency for business
But you must: Pay taxes on gains and report transactions over $10,000.
State-Level Considerations
Most states: Follow federal guidance with no additional restrictions New York: Requires special “BitLicense” for cryptocurrency businesses
Some states: Have additional consumer protection laws No states: Currently ban cryptocurrency for individuals
European Union: Legal with Comprehensive Regulation

The EU approach: Comprehensive regulation through Markets in Crypto Assets (MiCA) framework.
Current Legal Status
Individual use: Completely legal across all EU member countries Business use: Legal with licensing requirements for crypto services Taxation: Each member country sets own tax rules Consumer protection: Strong regulatory framework protecting users
What EU Residents Can Do
✅ Buy and sell cryptocurrency legally
✅ Use licensed cryptocurrency exchanges
✅ Run cryptocurrency businesses with proper licensing
✅ Mine cryptocurrency (though some countries restrict energy-intensive mining)
Key requirement: Use only licensed exchanges and service providers.
Notable Member Country Specifics
Germany: Very crypto-friendly, clear tax guidance France: Legal with comprehensive business licensing Netherlands: Legal with strong consumer protection
Portugal: Very favorable tax treatment for individuals
Canada: Legal and Well-Regulated

Canada’s position: Cryptocurrency is legal and treated as either currency or commodity depending on use.
Regulatory Framework
Personal use: Legal, treated as commodity for tax purposes Business use: Must register as Money Service Business (MSB) Exchanges: Must comply with anti-money laundering regulations Taxation: Capital gains tax applies to cryptocurrency profits
Canadian Cryptocurrency Rights
✅ Legal to buy, sell, and hold cryptocurrency
✅ Legal to mine cryptocurrency
✅ Legal to accept cryptocurrency in business
✅ Legal to trade cryptocurrency
Tax obligation: Must report capital gains on cryptocurrency profits.
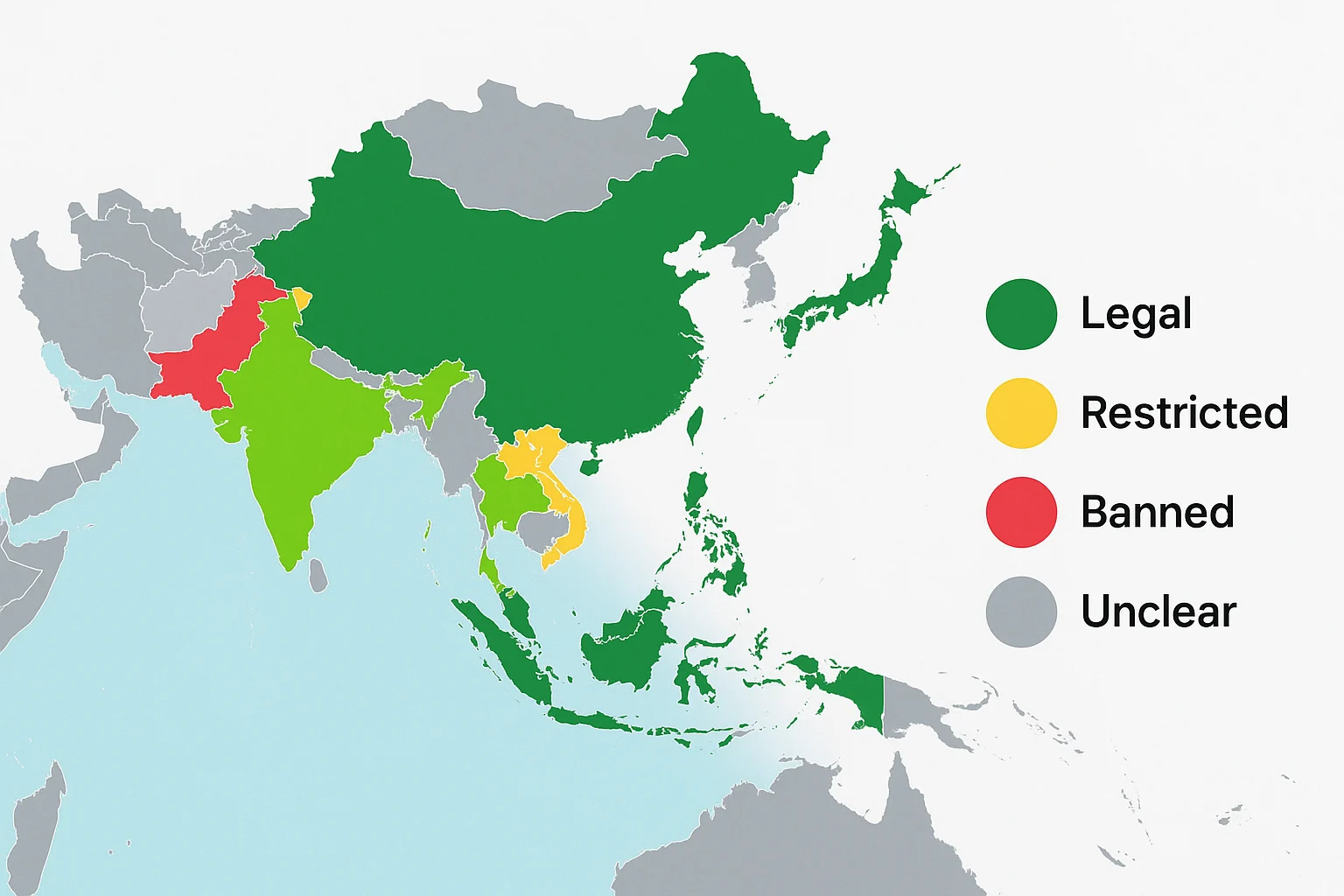
Asia-Pacific: Mixed Landscape
Japan: Pioneer in Crypto Regulation
Legal status: Cryptocurrency is legal and recognized as a method of payment Licensing: Exchanges must be licensed by Financial Services Agency Taxation: Clear tax framework for individuals and businesses Innovation hub: Government actively supports blockchain development
Australia: Legal with Tax Reporting
Legal status: Cryptocurrency is legal and treated as property Business registration: Cryptocurrency exchanges must register with AUSTRAC Taxation: Capital gains tax applies to cryptocurrency transactions Innovation support: Government supports blockchain technology development
Singapore: Crypto-Friendly Hub
Legal status: Cryptocurrency is legal for individuals and businesses Regulatory clarity: Clear guidelines for cryptocurrency services Business licensing: Cryptocurrency businesses must obtain licenses Tax efficiency: Favorable tax treatment for certain cryptocurrency activities
South Korea: Legal with Restrictions
Legal status: Cryptocurrency is legal but heavily regulated Exchange requirements: Only licensed exchanges allowed Real-name verification: Must use real names for all transactions Tax implications: Cryptocurrency gains subject to taxation
Countries with Restrictions or Bans

China: Complex and Changing
Current status: Cryptocurrency trading and mining banned, but holding may be legal Central Bank Digital Currency: China developing its own digital yuan Enforcement: Aggressive crackdown on cryptocurrency businesses Future uncertainty: Policy could change as digital yuan develops
India: Evolving Regulation
Current status: Legal to hold, but banking restrictions make trading difficult Regulatory development: Government working on comprehensive cryptocurrency law Taxation: High tax rates on cryptocurrency gains Future direction: Likely toward regulation rather than prohibition
Russia: Uncertain and Changing
Current status: Legal to hold, restricted for payments Business restrictions: Cryptocurrency businesses face limitations Sanctions impact: International sanctions affecting cryptocurrency access Regulatory uncertainty: Laws frequently changing
What “Legal” Actually Means for Different Activities

Buying Cryptocurrency
Legal in: US, Canada, EU, Japan, Australia, Singapore, most developed countries Restricted in: Some countries require using only licensed exchanges Banned in: Bangladesh, Algeria, Egypt, Iraq, Morocco, Nepal
Selling Cryptocurrency
Legal in: Same countries where buying is legal Tax implications: Must report capital gains in most countries Licensing requirements: Large-scale selling may require business licenses
Mining Cryptocurrency
Legal in: Most countries where cryptocurrency is legal Energy restrictions: Some countries limit mining due to electricity consumption Business registration: Commercial mining may require business licenses Environmental considerations: Some jurisdictions restricting energy-intensive mining
Using Cryptocurrency for Payments
Legal in: Japan, Germany, some US states, various other countries Limited acceptance: Legal but few merchants accept it Regulatory gray areas: Some countries unclear on payment usage
Running Cryptocurrency Businesses
Licensing required: Most countries require special licenses for exchanges and services Compliance obligations: Must follow anti-money laundering and tax reporting rules Consumer protection: Must provide certain protections for customers
Different types of cryptocurrency may have different legal classifications.
Tax Implications: The Legal Requirement Everyone Forgets

Here’s the reality: Even where cryptocurrency is completely legal, you still owe taxes.
United States Tax Requirements
Capital gains tax: Owe taxes when selling cryptocurrency for profit Trading taxes: Each crypto-to-crypto trade is a taxable event Mining income: Newly mined cryptocurrency counts as income Record keeping: Must track basis and holding periods for all transactions
International Tax Considerations
Reporting thresholds: Most countries require reporting large cryptocurrency transactions Double taxation: May owe taxes in multiple countries Foreign account reporting: Cryptocurrency holdings may need to be reported to tax authorities
Critical point: Cryptocurrency legality doesn’t eliminate tax obligations.
How to Stay Legal: Compliance Best Practices

Research Your Local Laws
Check current regulations: Laws change frequently in this space Understand tax obligations: Know what you owe and when Use licensed services: Only use regulated exchanges and service providers Keep detailed records: Track all transactions for tax reporting
Choose Regulated Platforms
Using the best cryptocurrency apps for beginners often means choosing regulated options.
Licensed exchanges: Use only exchanges licensed in your jurisdiction Compliance features: Choose platforms that provide tax reporting tools Insurance coverage: Prefer platforms that offer some form of user protection
Trade safely on Kraken, a fully licensed and regulated exchange
Maintain Proper Records
Transaction history: Keep records of all buys, sells, and trades Cost basis tracking: Know what you paid for each cryptocurrency Date tracking: Record dates for tax calculation purposes Exchange records: Download and save all exchange transaction histories
Understand Reporting Requirements
Annual tax filing: Report cryptocurrency gains and losses Large transaction reporting: Some countries require reporting transactions over certain amounts Foreign account reporting: May need to report foreign cryptocurrency holdings Business licensing: Get appropriate licenses if running cryptocurrency business
Red Flags: What Could Get You in Legal Trouble

Activities to Avoid
Using unlicensed exchanges: Especially in countries with licensing requirements Not reporting taxes: Tax evasion is illegal regardless of asset type Money laundering: Using cryptocurrency to hide illegal income sources Securities violations: Promoting unregistered cryptocurrency investments Sanctions violations: Using cryptocurrency to evade international sanctions
Gray Area Activities
Privacy coins: Some countries restricting anonymous cryptocurrencies DeFi protocols: Regulatory status unclear in many jurisdictions Cross-border transfers: Large amounts may trigger reporting requirements Business payments: Unclear regulations in some countries
Understanding cryptocurrency risks includes legal and regulatory risks.
Future Legal Developments: What’s Coming

Regulatory Trends
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Governments creating their own digital currencies Stablecoin regulation: Increased oversight of dollar-backed cryptocurrencies DeFi regulation: Rules for decentralized finance protocols being developed Cross-border coordination: International cooperation on cryptocurrency regulation
What This Means for Users
Increased clarity: Clearer rules for legal cryptocurrency use Consumer protection: Better protection for cryptocurrency users Compliance requirements: More reporting and compliance obligations Mainstream adoption: Regulation enabling broader business acceptance
Common Legal Questions Answered

Q: Can the government seize my cryptocurrency? A: Governments can seize cryptocurrency involved in illegal activities, just like any other asset. Legal holdings are generally protected.
Q: Do I need to report cryptocurrency on tax returns? A: In most countries, yes. Cryptocurrency gains are taxable in most jurisdictions.
Q: Can I use cryptocurrency for business? A: In most countries where cryptocurrency is legal, yes. You may need business licenses and must follow tax rules.
Q: What if I bought cryptocurrency before it was regulated? A: Retroactive criminalization is rare. Most new regulations don’t apply to past legal activities.
Q: Can cryptocurrency legality change overnight? A: Sudden changes are unusual in developed countries. Most regulatory changes have transition periods.
Staying Informed: Legal Resources
![]()
Official Sources
Government websites: IRS (US), CRA (Canada), FCA (UK), BaFin (Germany) Regulatory agencies: SEC, CFTC, FinCEN in the US; similar agencies elsewhere Tax authorities: Official guidance on cryptocurrency taxation Legal databases: Government publications on cryptocurrency law
Professional Resources
Tax professionals: CPAs and tax attorneys familiar with cryptocurrency Legal advisors: Lawyers specializing in cryptocurrency law Compliance services: Companies providing regulatory compliance tools Industry associations: Organizations tracking regulatory developments
Educational Resources
Continue learning about cryptocurrency fundamentals
Understand how cryptocurrency works within legal frameworks
Learn about different types of legal cryptocurrency
Get expert guidance on cryptocurrency legality with Crypto Crew University courses
The Bottom Line: Legal in Most Places, Regulated Everywhere

Cryptocurrency is legal in most developed countries, but legal doesn’t mean unregulated.
Key takeaways:
- Legal to buy, sell, and hold in US, Canada, EU, Japan, Australia, and most developed nations
- Tax reporting required in virtually all countries where it’s legal
- Use only licensed exchanges and service providers in your jurisdiction
- Keep detailed records for tax compliance
- Stay informed about changing regulations
The legal landscape is stabilizing toward regulation rather than prohibition. Governments want to control and tax cryptocurrency, not eliminate it.
Your responsibility: Stay informed, use legal services, and comply with tax obligations. Understanding the differences between cryptocurrency and traditional money helps you navigate the legal requirements.
The future is increasingly clear: Cryptocurrency is becoming a regulated part of the mainstream financial system. Learn to use it legally and you’ll be ahead of the curve.
This article provides general information about cryptocurrency legality and should not be considered legal advice. Cryptocurrency laws change frequently and vary by jurisdiction. Consult with qualified legal and tax professionals for advice specific to your situation.
