Bridge Token
Bridge Token: Cross-Chain Asset Representations
Bridge tokens are wrapped versions of assets that exist on different blockchains through cross-chain bridge protocols. They’re like having dollars that work in different countries’ ATM systems.
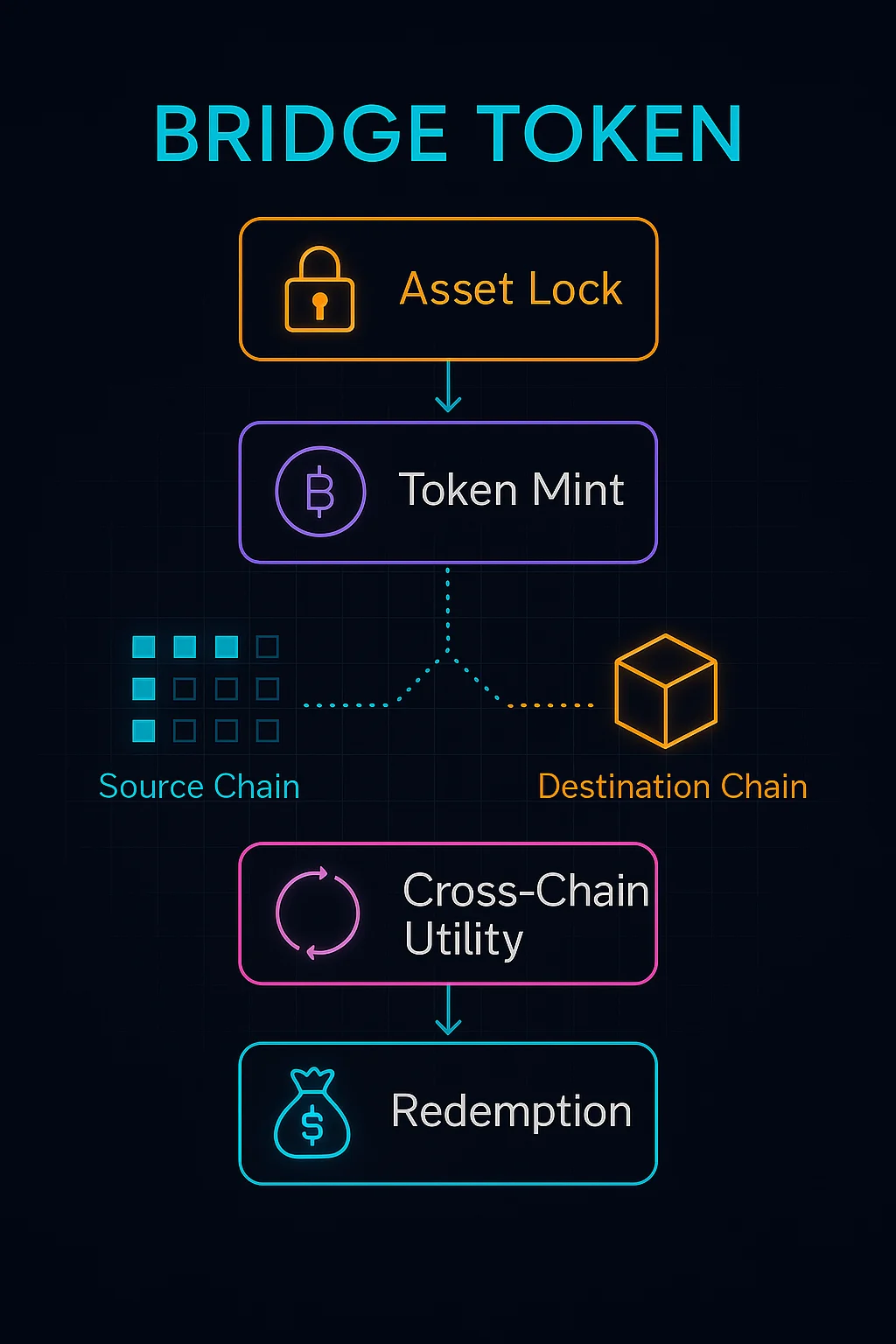
A bridge token is a representation of an asset from one blockchain that can be used on a different blockchain through cross-chain bridge infrastructure. The original asset gets locked while an equivalent token gets minted on the destination chain.
How Bridge Tokens Work
Asset locking secures original tokens in smart contracts or custody solutions while equivalent bridge tokens get minted on destination chains.
Peg maintenance ensures bridge tokens maintain 1:1 value with underlying assets through arbitrage mechanisms and redemption guarantees.
Cross-chain liquidity enables using assets across multiple blockchains without selling and repurchasing on each chain separately.
Real-World Examples
- Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) enables Bitcoin usage in Ethereum DeFi applications
- Portal tokens from Wormhole bridge enable asset movement across multiple chains
- Polygon bridge tokens provide Ethereum asset access on Polygon’s faster, cheaper network
Why Beginners Should Care
Expanded utility for assets by enabling use across multiple blockchain ecosystems without complex trading procedures.
Bridge risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, custody failures, or validator misbehavior that could result in bridge token depeg or loss.
Liquidity fragmentation as bridge tokens may have different trading volumes and prices across various chains and exchanges.
Related Terms: Cross-Chain Bridge, Wrapped Token, Peg Mechanism, Asset Locking
