Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP)
Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP): Manipulation-Resistant Pricing
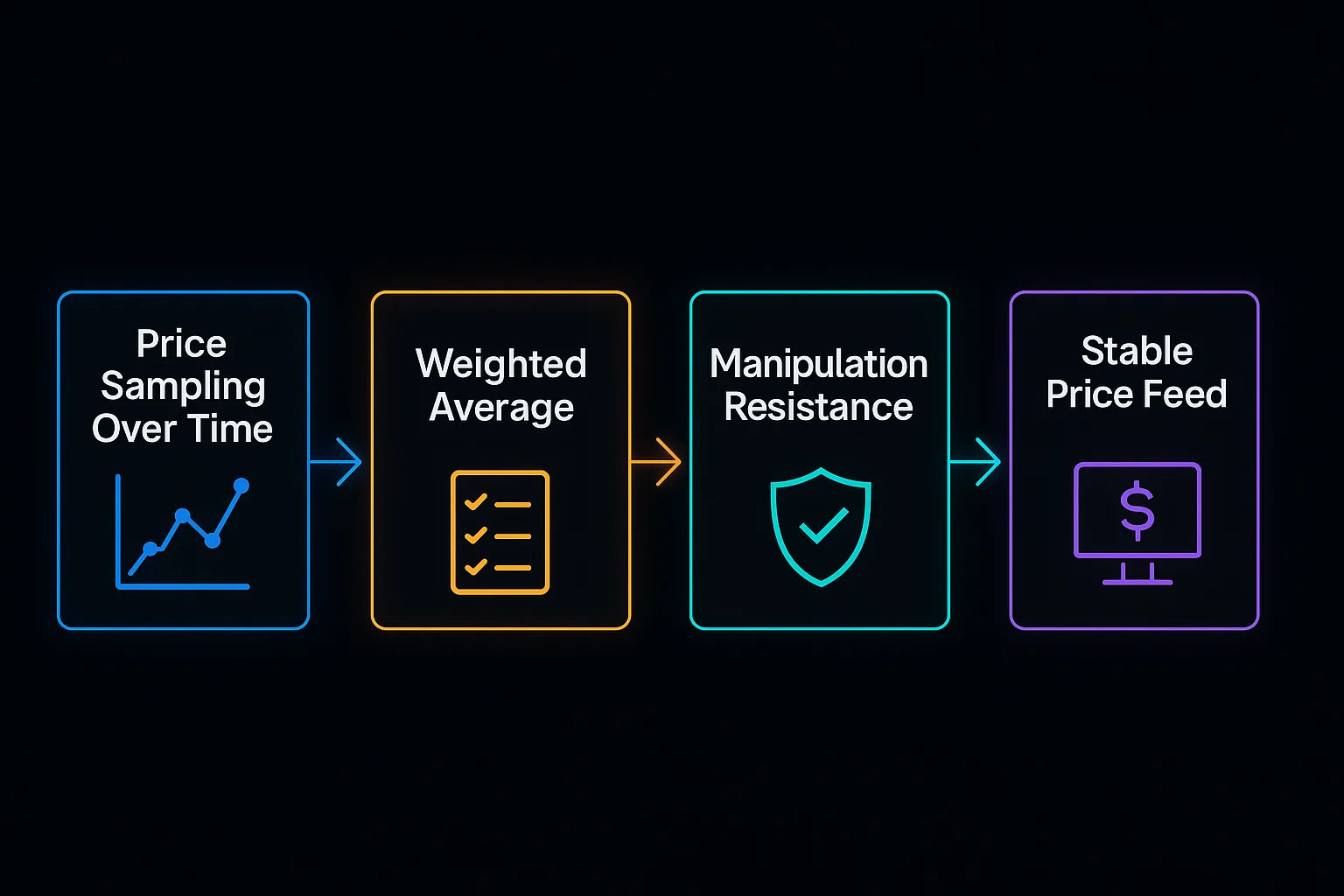
TWAP calculates asset prices over extended time periods to resist manipulation and provide more stable price references for protocols. It’s like taking your temperature every hour instead of just once.
Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) is a pricing mechanism that calculates the average price of an asset over a specific time period, reducing the impact of short-term price manipulation. TWAP oracles provide more stable price feeds for DeFi protocols.
How TWAP Works
Continuous sampling records asset prices at regular intervals throughout the measurement period rather than relying on single point-in-time prices.
Weighted averaging gives equal weight to each time period, preventing large trades or manipulation attempts from skewing the overall price calculation.
Manipulation resistance makes it expensive and difficult for attackers to influence TWAP prices since they would need to sustain artificial prices over extended periods.
Real-World Examples
- Uniswap V2/V3 provides TWAP oracles that many protocols use for price feeds
- MakerDAO uses TWAP prices to prevent flash loan attacks on collateral valuations
- Compound leverages TWAP pricing to resist oracle manipulation in lending markets
Why Beginners Should Care
Protocol security depends on manipulation-resistant price feeds to prevent flash loan attacks and other exploitation attempts.
Stable liquidations using TWAP prevents users from being liquidated due to temporary price spikes or manipulation.
Lagging prices mean TWAP feeds may not reflect rapid legitimate price movements, potentially affecting trading efficiency.
Related Terms: Oracle, Price Manipulation, Flash Loan Attack, Price Feed
