Encrypted Mempool
Encrypted Mempool: Private Transaction Pools
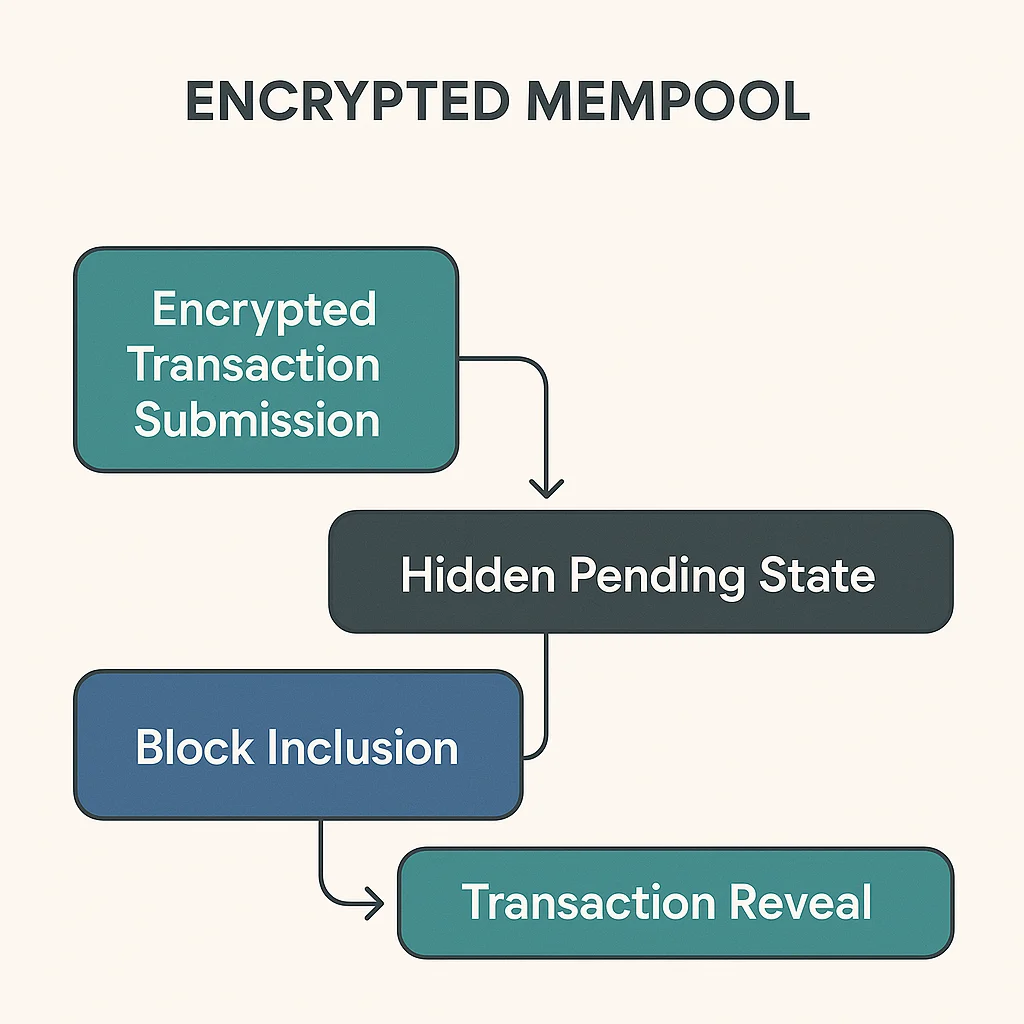
Encrypted mempools hide transaction details until inclusion in blocks, preventing front-running and MEV extraction. It’s like sending sealed bids instead of announcing your strategy publicly.
An encrypted mempool contains pending transactions that are cryptographically hidden from public view until block inclusion. This prevents sophisticated actors from front-running or extracting MEV from regular users’ transactions.
How Encrypted Mempools Work
Cryptographic hiding conceals transaction details like amounts, tokens, and intended actions until validators include them in blocks.
Commit-reveal schemes require users to first commit to encrypted transactions, then reveal details after inclusion to prevent front-running.
Threshold decryption may require multiple parties to collaborate in revealing transaction details, preventing single-party censorship.
Real-World Examples
- Flashbots Protect provides MEV protection through private transaction pools
- Shutter Network develops threshold encryption for Ethereum transactions
- Aztec Network uses encrypted state for privacy-preserving smart contracts
Why Beginners Should Care
MEV protection significantly reduces the hidden tax on DeFi transactions that bots extract through front-running and sandwich attacks.
Fairer markets emerge when sophisticated actors can’t see pending transactions and position themselves advantageously.
Privacy enhancement protects trading strategies and financial information from public blockchain surveillance.
Related Terms: MEV, Front-Running, Private Mempool, Threshold Encryption
