Atomic Swap
Atomic Swap: Trustless Cross-Chain Trading
Atomic swaps enable direct trading between different cryptocurrencies without exchanges or intermediaries. Either both trades complete successfully, or neither happens – no middle ground.
An atomic swap is a smart contract technology that enables the exchange of cryptocurrencies from different blockchains without requiring a trusted third party. The swap either completes entirely for both parties or fails completely, preventing partial execution.
How Atomic Swaps Work
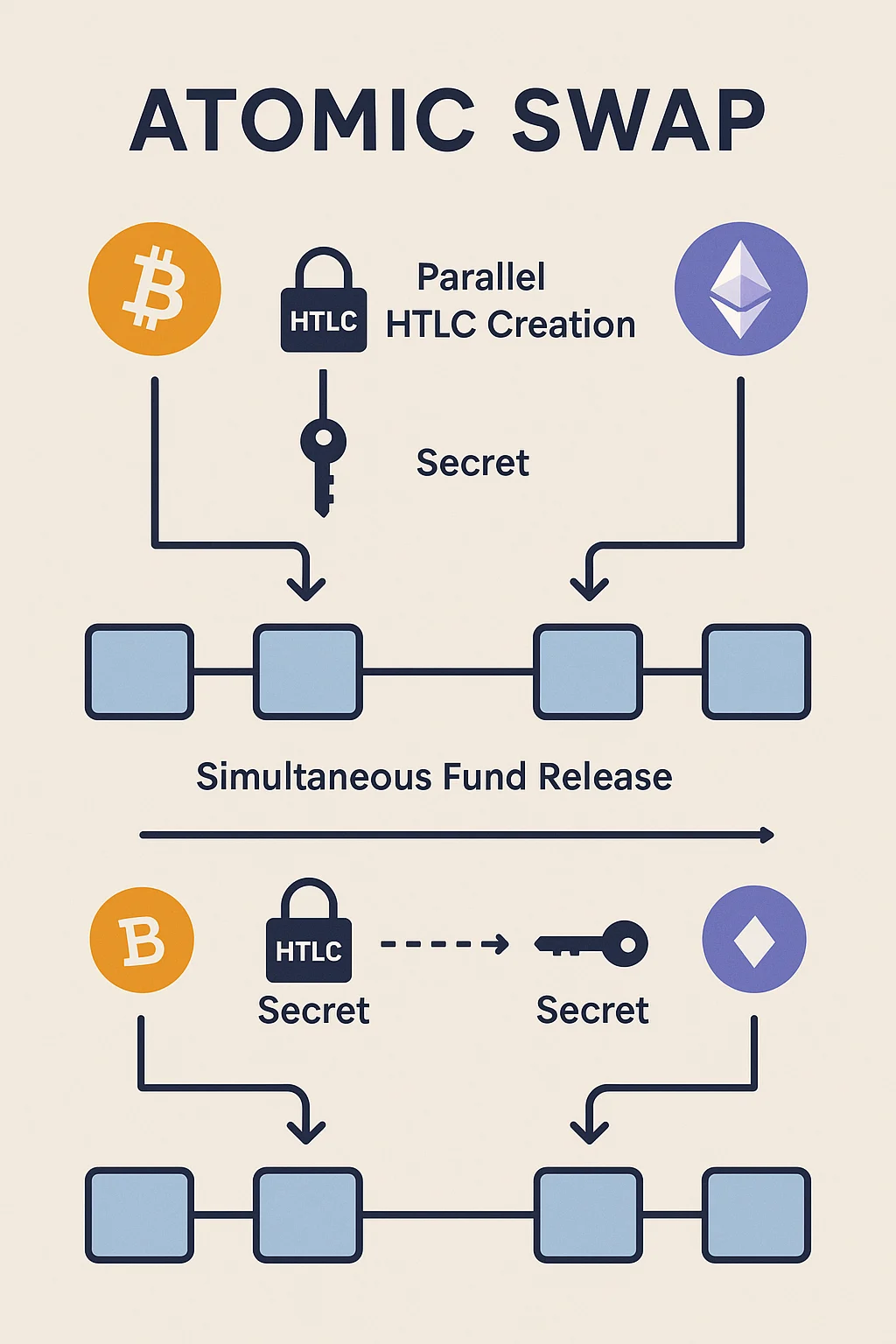
Hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs) create conditional payments that require cryptographic proof to unlock funds within specific time limits. This ensures both parties fulfill their obligations.
Cross-chain compatibility requires both cryptocurrencies to support the same hashing algorithm and basic smart contract functionality for the swap mechanism to work.
Time locks prevent one party from receiving funds without completing their side of the trade. If the swap isn’t completed within the time limit, both parties can reclaim their original funds.
Real-World Examples
- Lightning Network enables Bitcoin atomic swaps with compatible cryptocurrencies
- Komodo pioneered atomic swap technology for cross-chain decentralized exchange
- Ethereum-Bitcoin swaps require specialized implementations due to different scripting capabilities
Why Beginners Should Care
Decentralized trading eliminates counterparty risk from centralized exchanges while enabling direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains.
Technical limitations currently restrict atomic swaps to cryptocurrencies with compatible features, excluding many popular tokens from direct swap capabilities.
User experience remains complex compared to centralized exchanges, requiring technical knowledge and longer settlement times for successful swaps.
Related Terms: Smart Contract, Cross-Chain, HTLC, DEX
