Sidechain
Sidechain: Independent Chains with Main Chain Connections
Sidechains operate independently while maintaining bridges to main blockchains. They’re like having a separate express lane that connects back to the main highway when needed.
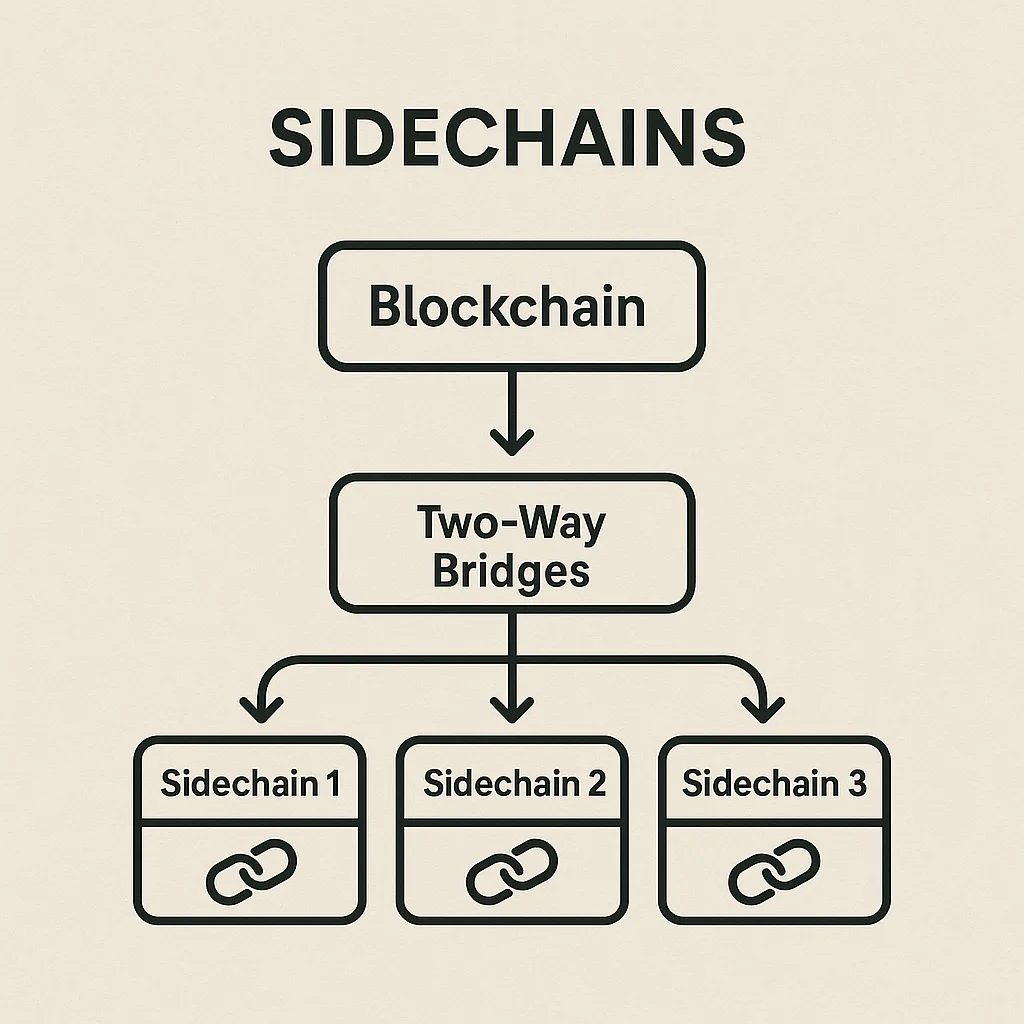
A sidechain is an independent blockchain that runs parallel to a main blockchain and is connected through a two-way bridge allowing asset transfers. Sidechains can have different consensus mechanisms, block times, and features while maintaining interoperability with the parent chain.
How Sidechains Work
Two-way pegs lock assets on the main chain and mint equivalent tokens on the sidechain, enabling transfers between chains. When moving back, sidechain tokens are burned and main chain assets are unlocked.
Independent consensus allows sidechains to optimize for specific use cases like faster transactions, lower fees, or specialized smart contract features without affecting the main chain.
Bridge security varies from centralized custodians to complex multi-signature schemes to fully decentralized smart contract systems, each with different trust assumptions.
Real-World Examples
- Polygon – Popular Ethereum sidechain offering faster, cheaper transactions
- xDai Chain – Stablecoin-based sidechain for everyday payments
- Liquid Network – Bitcoin sidechain for faster settlement between exchanges
Why Beginners Should Care
Lower costs on sidechains make them attractive for testing DeFi protocols or making frequent transactions without expensive main chain fees.
Bridge risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, centralized custody risks, and potential loss of funds if bridge mechanisms fail or get hacked.
Ecosystem fragmentation can occur when liquidity and users move to sidechains, potentially weakening the main chain’s network effects.
Related Terms: Bridge, Layer 2, Two-Way Peg, Interoperability
