Blockchain
Blockchain: The Unchangeable Digital Ledger
Forget the hype – blockchain is simply a better way to keep records. It’s like a ledger book that everyone can see, but no one can cheat.
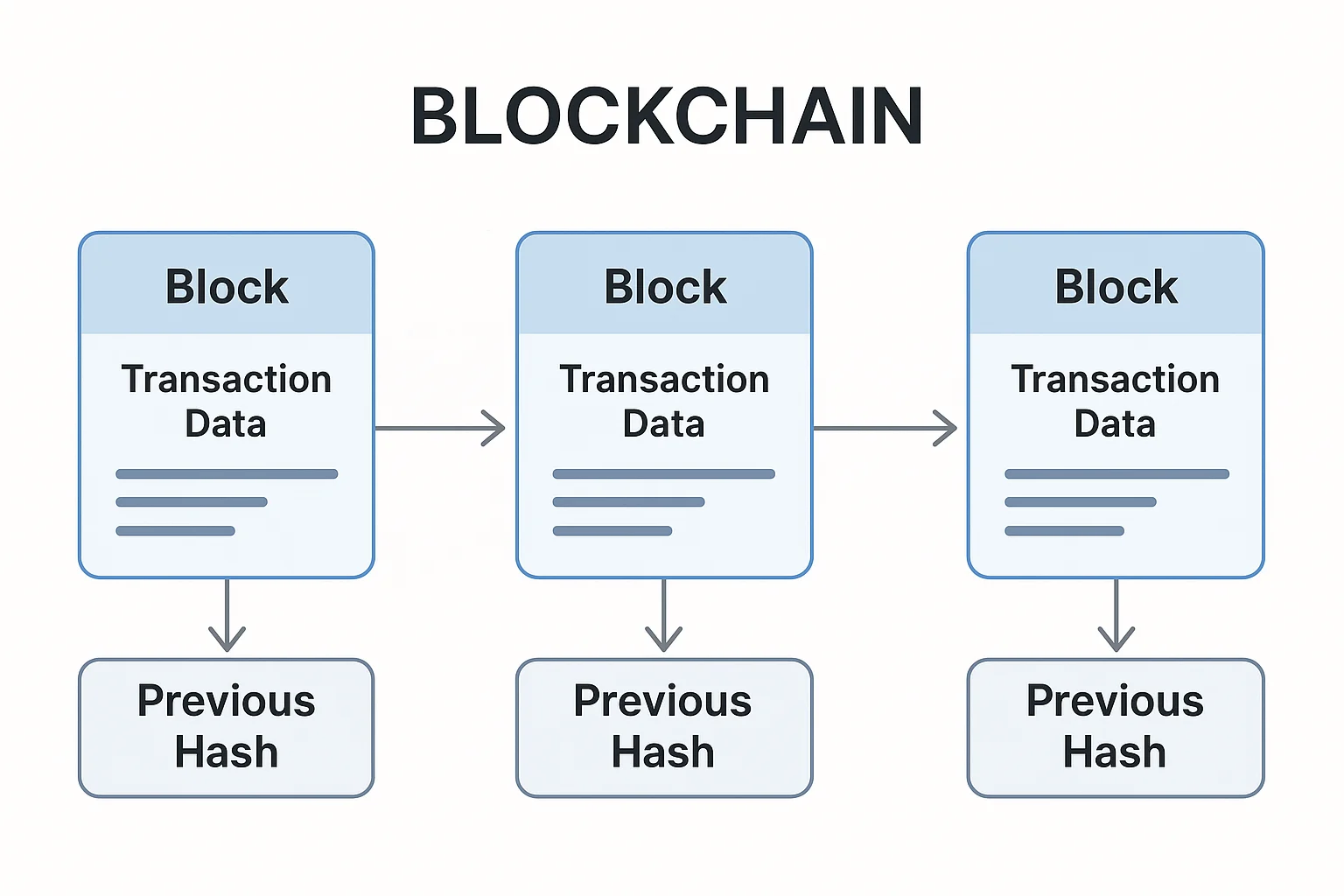
Blockchain is a chain of digital records (blocks) that are linked together and secured using cryptography. Once information goes into a block, changing it becomes practically impossible without changing every subsequent block.
How Blockchain Works
Picture a notebook where every page is numbered and contains a summary of the previous page. To fake page 50, you’d need to rewrite every page from 50 to the end – while thousands of people are watching and comparing their copies.
Each block contains transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic fingerprint of the previous block. This creates an unbreakable chain of records.
New blocks get added roughly every 10 minutes (for Bitcoin), and thousands of computers worldwide verify each addition.
Real-World Examples
- Bitcoin blockchain processes about 300,000 transactions daily
- Ethereum blockchain powers thousands of decentralized applications
- Supply chain tracking helps verify authentic products from counterfeits
Why Beginners Should Care
Blockchain eliminates the need for trusted intermediaries. Banks, governments, and corporations can’t manipulate blockchain records without everyone noticing.
This transparency creates opportunities for fair financial systems, transparent voting, authentic product verification, and ownership records that can’t be disputed.
Related Terms: Bitcoin, Mining, Consensus Mechanism, Hash Rate
