Sharding
Sharding: Splitting Networks for Speed
Sharding divides blockchain networks into smaller pieces that process transactions in parallel. It’s like adding more checkout lanes at the grocery store – same capacity, faster service.
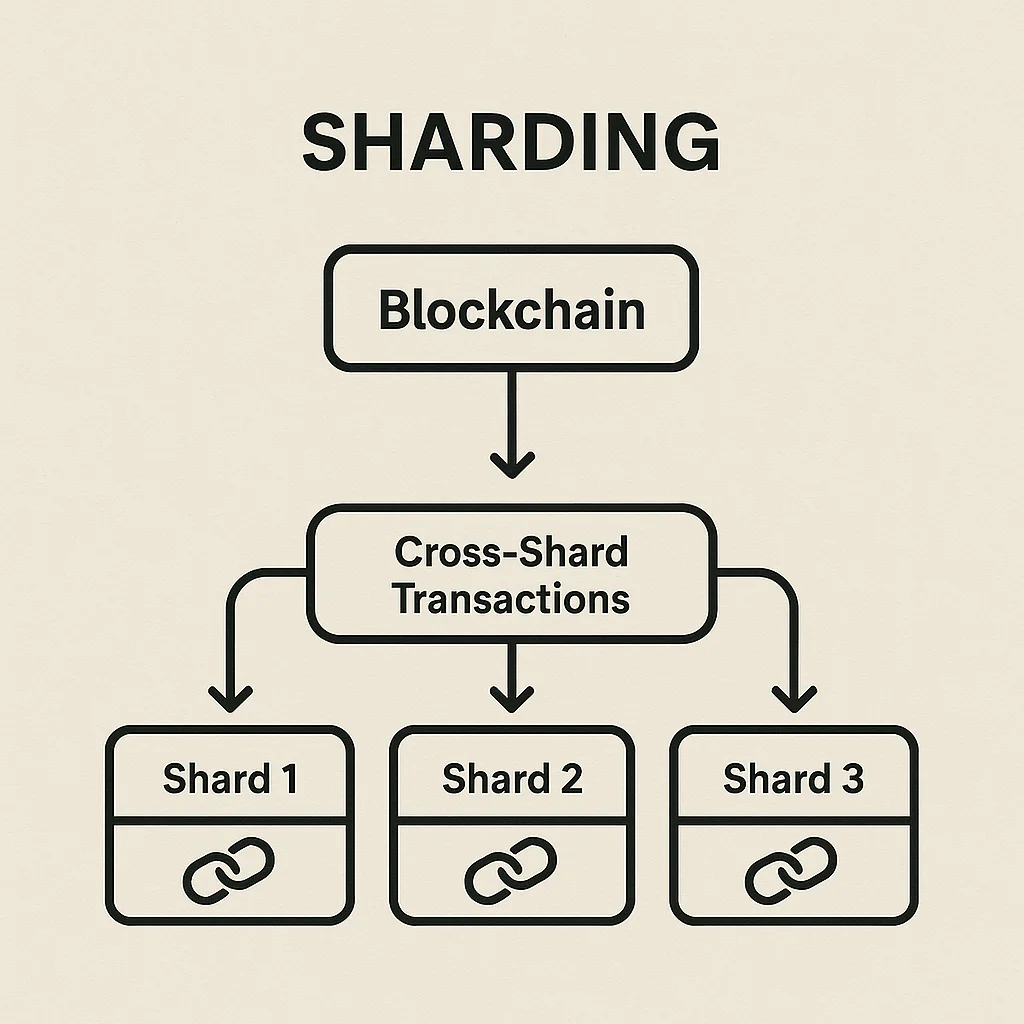
Sharding is a scaling technique that splits a blockchain network into smaller, parallel chains called shards that process transactions independently. Each shard handles a subset of all transactions, dramatically increasing total network throughput.
How Sharding Works
Parallel processing allows multiple shards to process different transactions simultaneously instead of every node processing every transaction sequentially.
State partitioning divides account balances and smart contract data across shards so that most transactions only need to touch one shard for validation.
Cross-shard communication handles transactions that involve accounts or contracts on different shards, requiring coordination between multiple shard chains.
Real-World Examples
- Ethereum 2.0 plans 64 shard chains to increase transaction capacity dramatically
- Zilliqa implemented sharding from launch, processing thousands of transactions per second
- Near Protocol uses dynamic sharding that adjusts capacity based on network demand
Why Beginners Should Care
Scalability solutions like sharding aim to reduce transaction fees and confirmation times that currently limit blockchain adoption for everyday use.
Complexity increases with sharding as developers must consider cross-shard interactions and users might face different experiences depending on which shard their transactions use.
Security trade-offs exist since individual shards have less security than the full network, requiring careful design to prevent shard-specific attacks.
Related Terms: Layer 2, Scalability, Throughput, Cross-Chain
