Token Burn
Token Burn: Destroying Supply for Value
Token burns permanently remove cryptocurrency from circulation by sending it to addresses where it can never be recovered. It’s digital deflation in action.
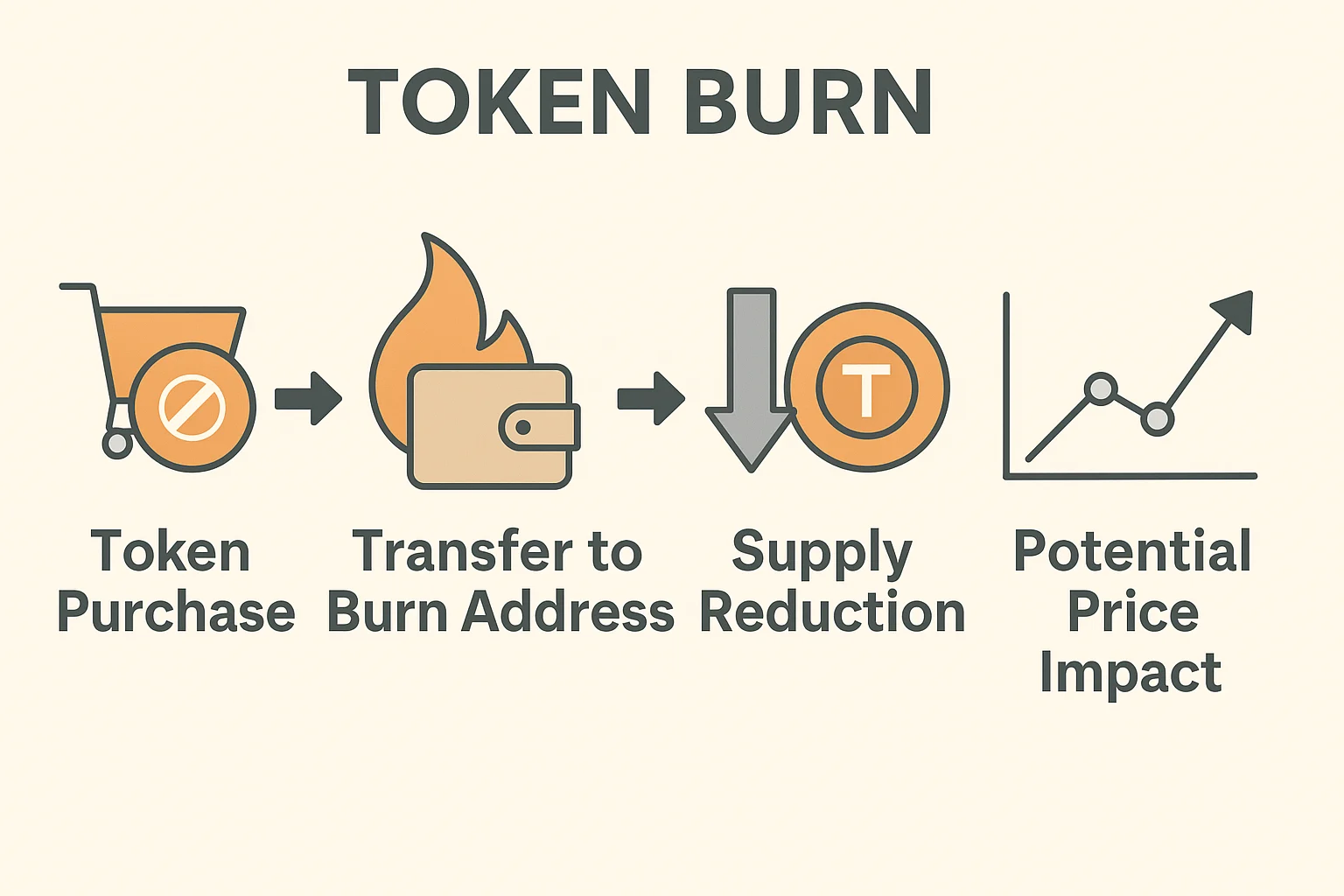
Token burn is the permanent removal of cryptocurrency tokens from circulation by sending them to an unusable address or smart contract that destroys them. This reduces total supply, potentially increasing the value of remaining tokens.
How Token Burns Work
Burn addresses are cryptocurrency addresses with no known private keys, ensuring sent tokens can never be retrieved. Bitcoin uses addresses like 1BitcoinEaterAddressDontSendf59kuE for provable burns.
Smart contract burns automatically destroy tokens through code, often triggered by specific events like transaction fees or governance votes.
Buyback and burn programs see projects purchase tokens from open markets then burn them, combining market buying pressure with supply reduction.
Real-World Examples
- Binance Coin (BNB) burns tokens quarterly based on exchange profits
- Ethereum EIP-1559 burns base fees from every transaction, making ETH deflationary during high usage
- Shiba Inu community-driven burns attempt to reduce massive token supply
Why Beginners Should Care
Supply and demand economics suggest that reducing supply while maintaining demand should increase token value, though this isn’t guaranteed in practice.
Marketing benefits from burns often create more price impact than the actual supply reduction, especially for tokens with large circulating supplies.
Sustainability questions arise when burn mechanisms depend on continuous project revenue or community participation that might not persist long-term.
Related Terms: Tokenomics, Supply, Deflationary, Buyback
