Restaking
Restaking: Double-Duty for Staked Assets
Restaking allows already-staked cryptocurrency to secure additional networks and earn extra rewards. It’s like getting paid twice for the same job, but with twice the risk.
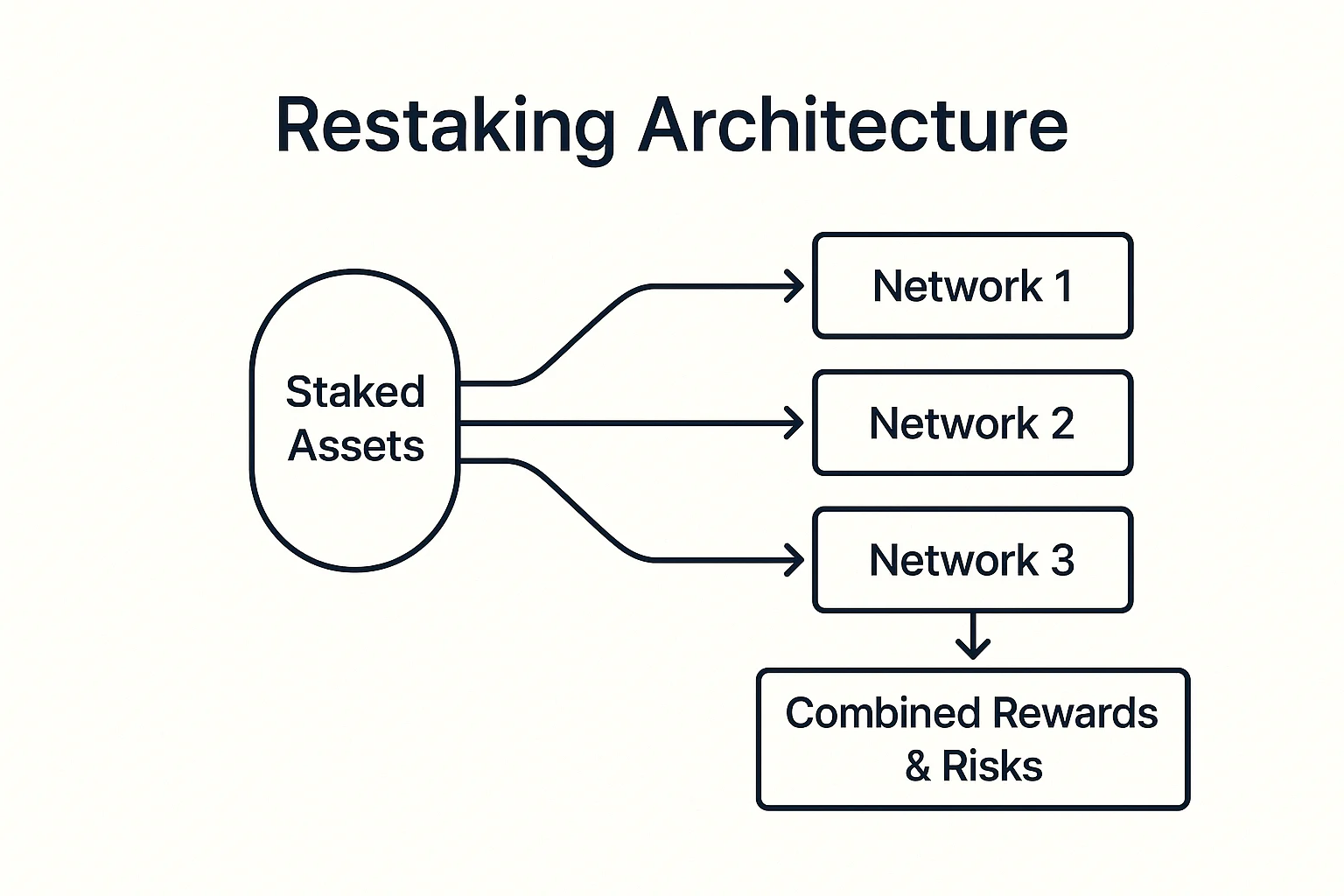
Restaking is a mechanism that allows staked cryptocurrency to simultaneously secure multiple networks or protocols, earning additional rewards beyond the base staking yield. Validators can opt into additional services while their stake continues securing the original network.
How Restaking Works
Dual security provisions enable staked assets to validate transactions on the primary network while also securing additional protocols or middleware services.
Slashing multiplication means validators face penalties from multiple sources if they misbehave, creating stronger incentives for honest behavior but higher risk exposure.
Reward stacking allows earning base staking rewards plus additional compensation from each extra service the validator provides to the ecosystem.
Real-World Examples
- EigenLayer enables Ethereum validators to restake ETH for securing additional protocols
- Babylon allows Bitcoin holders to stake their BTC for securing Proof-of-Stake networks
- Middleware protocols use restaking to bootstrap security from established validator sets
Why Beginners Should Care
Higher yields from restaking can significantly improve returns on staked assets, but come with proportionally increased risk of slashing penalties.
Complexity increases with multiple slashing conditions and service requirements that validators must understand and manage properly.
Early experimentation makes restaking protocols less proven than traditional staking, requiring careful risk assessment before committing significant funds.
Related Terms: Staking, Slashing, Validator, Yield Stacking
