Oracle
Oracle: Connecting Blockchains to Reality
Oracles are the bridges between blockchain smart contracts and real-world data. Without them, DeFi would be a closed system talking only to itself.
An oracle is a service that provides external data to blockchain networks, enabling smart contracts to access real-world information like prices, weather, sports scores, or any off-chain data. Blockchains can’t access external APIs directly, so oracles act as trusted data feeds.
How Oracles Work
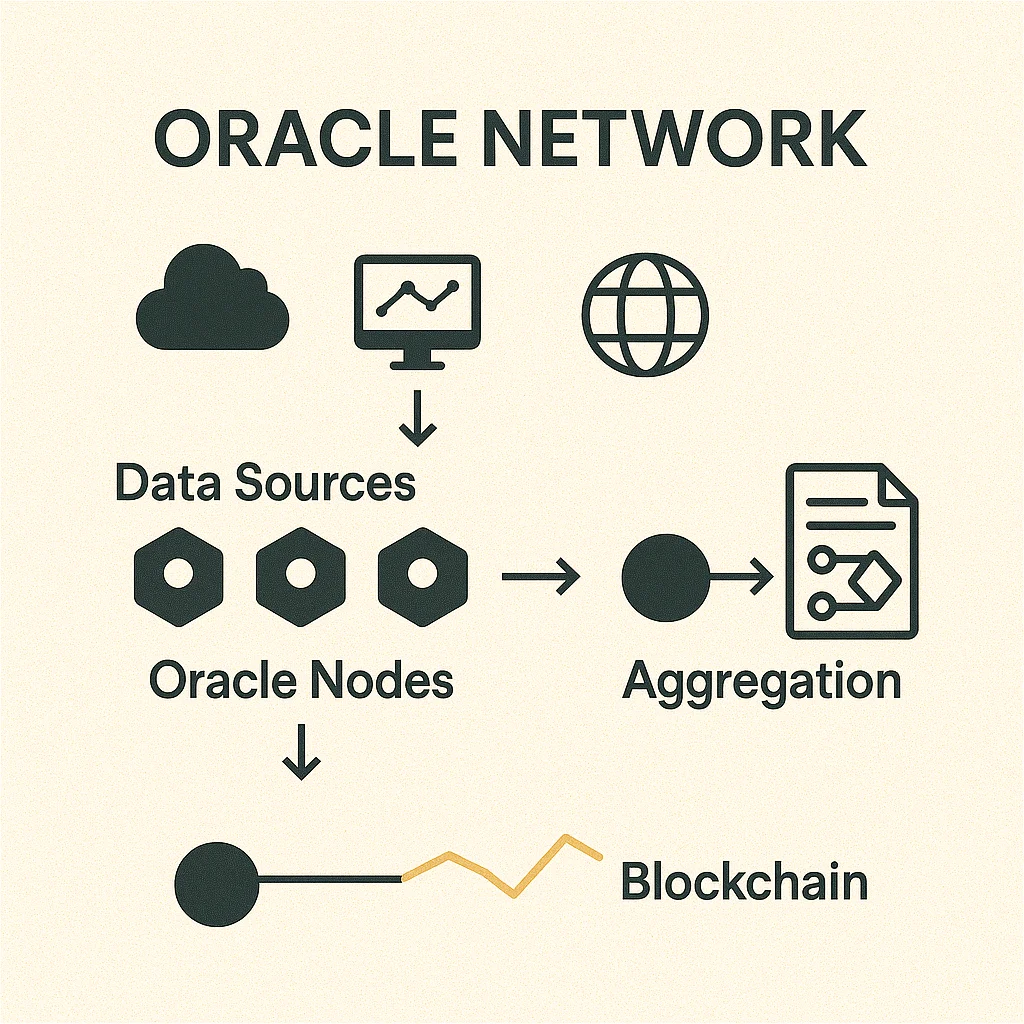
Data aggregation combines information from multiple sources to prevent single points of failure. Price oracles might average data from 10+ exchanges to provide accurate, manipulation-resistant feeds.
Cryptographic proofs ensure data integrity during transmission from external sources to blockchain networks. Oracles sign data with private keys that smart contracts can verify.
Decentralized oracle networks use multiple independent node operators to fetch and verify data, reducing risks of manipulation or single points of failure that plague centralized oracles.
Real-World Examples
- Chainlink – Largest oracle network providing price feeds to thousands of DeFi protocols
- Band Protocol – Cross-chain oracle solution supporting multiple blockchains
- Tellor – Decentralized oracle network secured by crypto-economic incentives
Why Beginners Should Care
Oracle failures can catastrophically break DeFi protocols. If price feeds fail or get manipulated, lending protocols can liquidate healthy positions or allow undercollateralized borrowing.
Oracle attacks have caused hundreds of millions in DeFi losses. Attackers manipulate price feeds to exploit smart contracts that rely on inaccurate data.
Choose DeFi protocols that use reputable, decentralized oracle solutions rather than single-source price feeds vulnerable to manipulation.
Related Terms: Smart Contract, DeFi, Price Feed, Chainlink
