Tor Network
Tor Network: Anonymous Internet Access
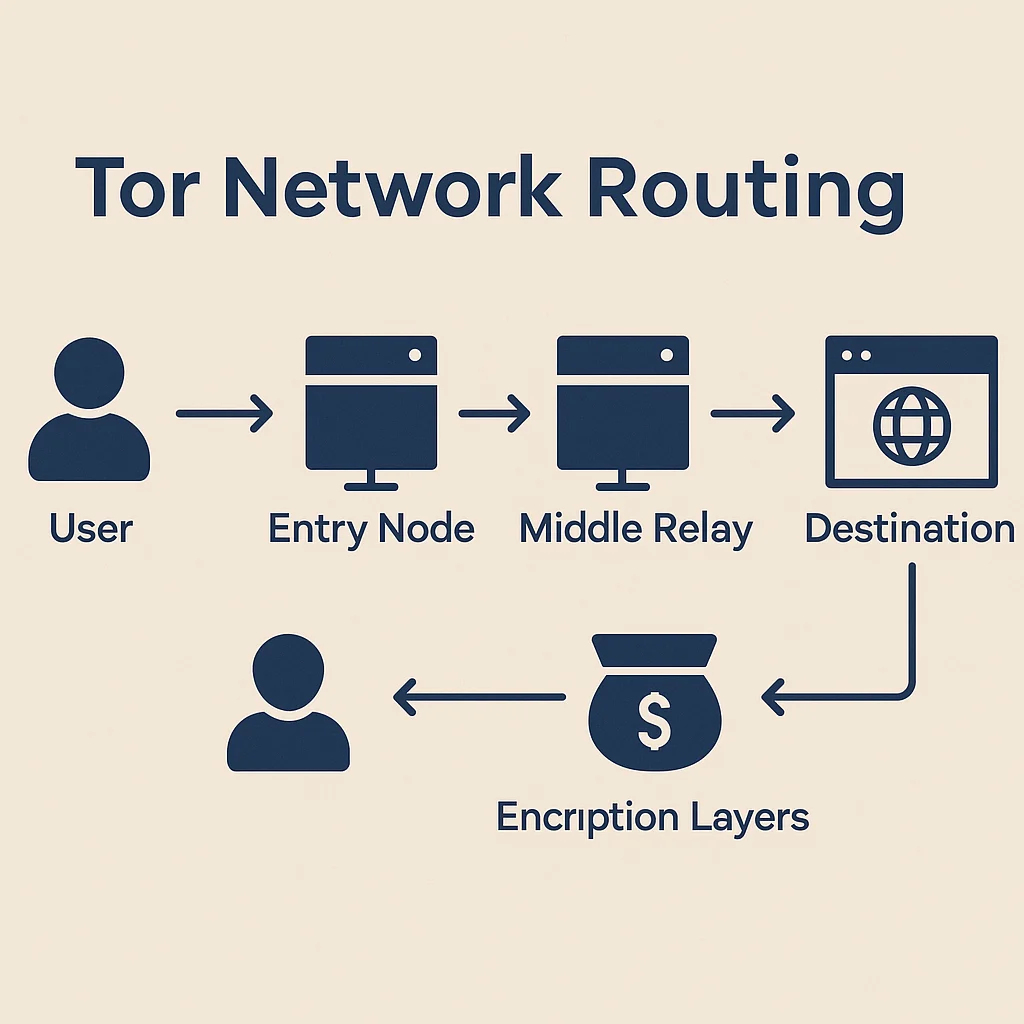
The Tor network routes internet traffic through multiple encrypted layers to hide user identity and location. It’s the digital equivalent of passing notes through a chain of people who don’t know the original sender.
The Tor network is a decentralized system of relay servers that encrypts and routes internet traffic through multiple hops to provide anonymous communication. Each relay only knows the previous and next step, preventing any single point from tracking complete connections.
How Tor Works
Onion routing encrypts data in multiple layers, with each relay removing one layer to reveal the next destination while keeping the original source hidden.
Three-hop minimum ensures no single relay knows both the source and destination of traffic, distributing trust across multiple independent operators worldwide.
Exit nodes decrypt the final layer and connect to regular internet services, potentially exposing the destination but not the original source of requests.
Real-World Examples
- Cryptocurrency users access exchanges and wallets through Tor to hide their IP addresses and locations
- Journalists and activists use Tor to communicate securely in oppressive regimes
- Dark web markets operate as Tor hidden services, though this represents a small fraction of Tor usage
Why Beginners Should Care
IP address protection prevents websites, ISPs, and governments from tracking your physical location when accessing cryptocurrency services.
Censorship resistance allows access to blocked websites and services in countries with restrictive internet policies.
Slower speeds and compatibility issues make Tor impractical for everyday browsing, but valuable for specific privacy-critical activities.
