Node
Node: The Network’s Backbone
Nodes are individual computers that maintain copies of the blockchain and enforce network rules. They’re the distributed infrastructure that makes cryptocurrency possible.
A node is a computer that participates in a blockchain network by maintaining a copy of the distributed ledger and relaying transactions. Nodes validate transactions, store blockchain history, and help maintain network decentralization.
How Nodes Work
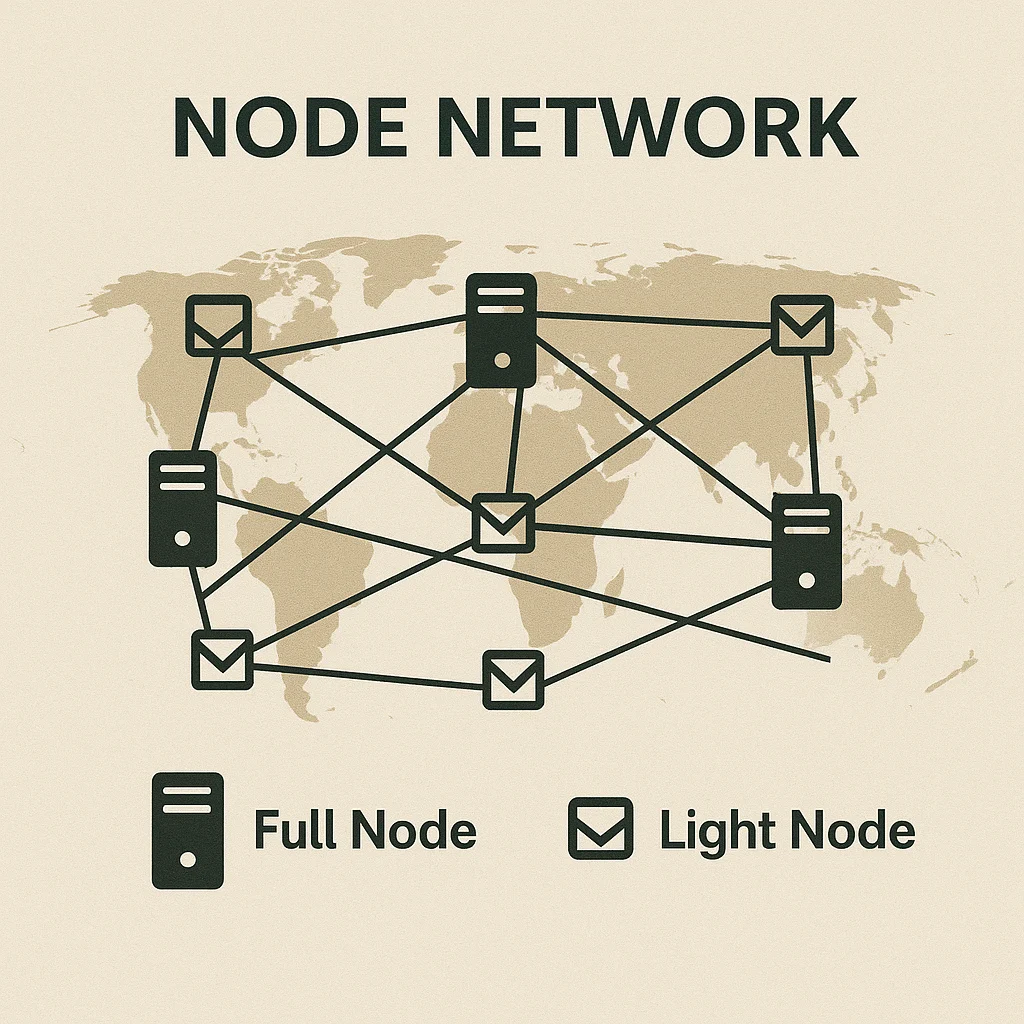
Full nodes download and validate every transaction and block in the blockchain’s history, ensuring all network rules are followed. They can independently verify the entire network state.
Light nodes (or SPV nodes) download only block headers and specific transactions they need, relying on full nodes for complete validation while using less storage and bandwidth.
Network communication happens through peer-to-peer connections where nodes share new transactions and blocks with their connected peers, propagating information across the entire network.
Real-World Examples
- Bitcoin Core – Reference implementation running on thousands of full nodes worldwide
- Ethereum Geth – Popular Ethereum node software maintaining network state
- Raspberry Pi nodes – Affordable home setups contributing to network decentralization
Why Beginners Should Care
Node diversity strengthens network decentralization and censorship resistance. More independent node operators mean less reliance on centralized infrastructure providers.
Running a node gives you direct access to the blockchain without trusting third parties like exchanges or wallet providers to give you accurate information.
Technical requirements include reliable internet, adequate storage (500GB+ for Bitcoin), and basic technical knowledge for setup and maintenance.
Related Terms: Full Node, Light Node, Peer-to-Peer, Decentralization
