Block Reward
Block Reward: Miner and Validator Compensation
Block rewards are the cryptocurrency payments that miners and validators receive for successfully adding new blocks to the blockchain. It’s how networks incentivize security without charging transaction fees.
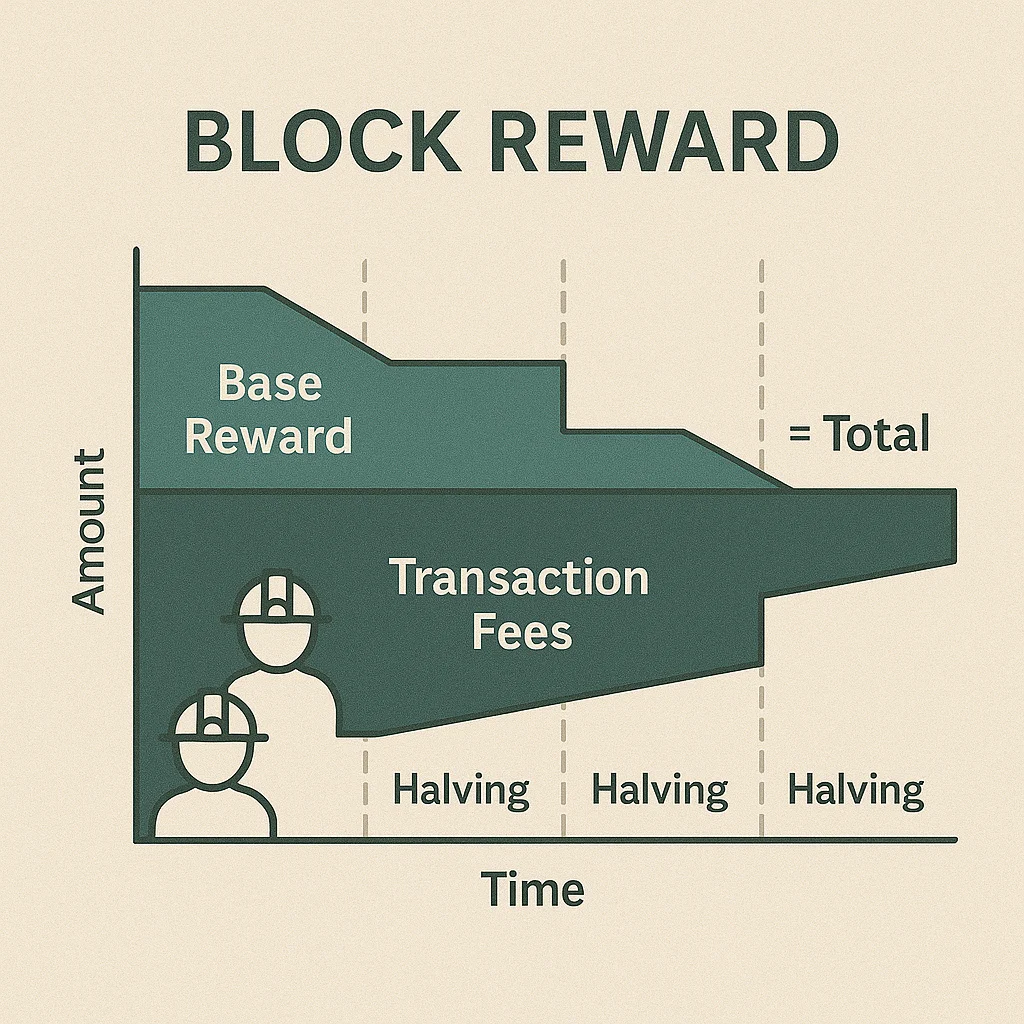
Block reward is the amount of cryptocurrency awarded to miners or validators for successfully creating and validating a new block on the blockchain. These rewards come from newly minted tokens and transaction fees included in the block.
How Block Rewards Work
New token creation through block rewards is often the primary way cryptocurrency enters circulation, following predetermined emission schedules rather than arbitrary printing.
Halving events reduce block rewards periodically to control inflation and maintain scarcity. Bitcoin halves rewards every 210,000 blocks, roughly every four years.
Fee supplements add transaction fees to base block rewards, creating variable compensation based on network usage and user willingness to pay for priority processing.
Real-World Examples
- Bitcoin currently awards 6.25 BTC per block (next halving to 3.125 BTC expected in 2024)
- Ethereum switched from mining rewards to staking rewards of ~6% annually
- Litecoin follows Bitcoin’s model with 12.5 LTC rewards that halve periodically
Why Beginners Should Care
Supply inflation from block rewards affects token economics and long-term value. Higher inflation rates can pressure prices downward if adoption doesn’t keep pace.
Network security depends on adequate block rewards to incentivize miners or validators. Insufficient rewards can lead to reduced security and potential attacks.
Investment timing around halving events often affects price speculation as reduced supply inflation meets existing demand.
Related Terms: Mining, Halving, Staking Rewards, Token Economics
