Halving
Halving: Cutting Block Rewards in Half
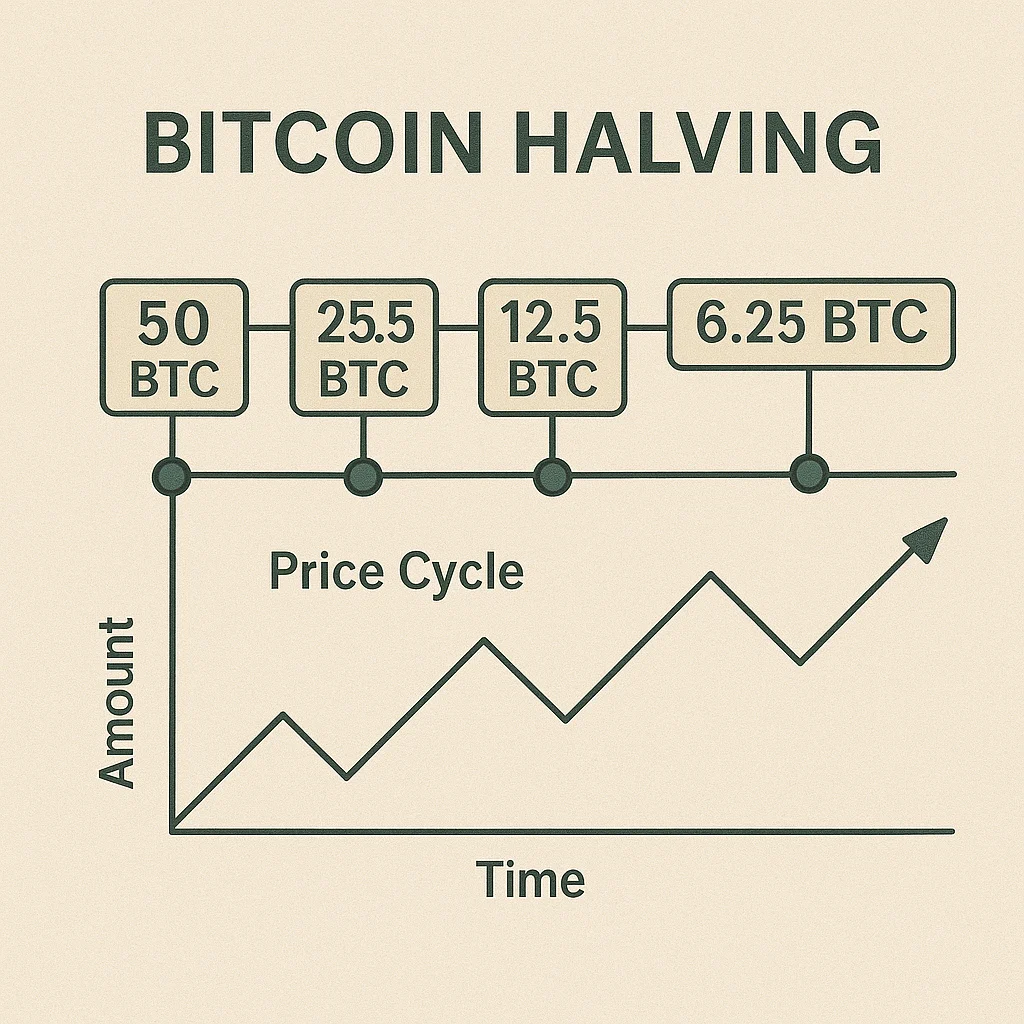
Halving events reduce block rewards by 50%, creating artificial scarcity that historically triggers major bull markets. It’s like cutting gold mining output in half overnight.
Halving is a pre-programmed event that reduces block rewards by half, typically occurring every four years or after a specific number of blocks. This mechanism controls inflation and maintains scarcity as networks mature and adoption grows.
How Halving Works
Scheduled reductions follow predetermined algorithms rather than human decisions, ensuring predictable monetary policy that can’t be manipulated by central authorities.
Supply shock occurs as new token creation suddenly drops by 50% while demand often remains constant or increases, creating upward pressure on prices.
Miner economics get disrupted as revenue cuts in half overnight. Less efficient miners may shut down, temporarily reducing network hash rate until difficulty adjusts.
Real-World Examples
- Bitcoin halvings in 2012, 2016, and 2020 each preceded major bull markets with 10-100x price increases
- Litecoin halving events follow similar patterns with smaller market impact due to lower adoption
- Bitcoin Cash inherited Bitcoin’s halving schedule after the 2017 fork
Why Beginners Should Care
Price speculation often surrounds halving events as reduced supply meets existing demand, though past performance doesn’t guarantee future results.
Market timing strategies attempt to position for halving-driven price increases, but timing markets remains extremely difficult even with predictable supply changes.
Long-term scarcity increases through halving until block rewards become negligible and transaction fees become the primary miner incentive.
Related Terms: Block Reward, Mining, Supply Shock, Bull Market
