Hard Fork
Hard Fork: Splitting the Blockchain
Hard forks create permanent splits in blockchain networks, often resulting in two separate cryptocurrencies. They’re like corporate divorces – messy, dramatic, and usually involving lots of arguing about money.
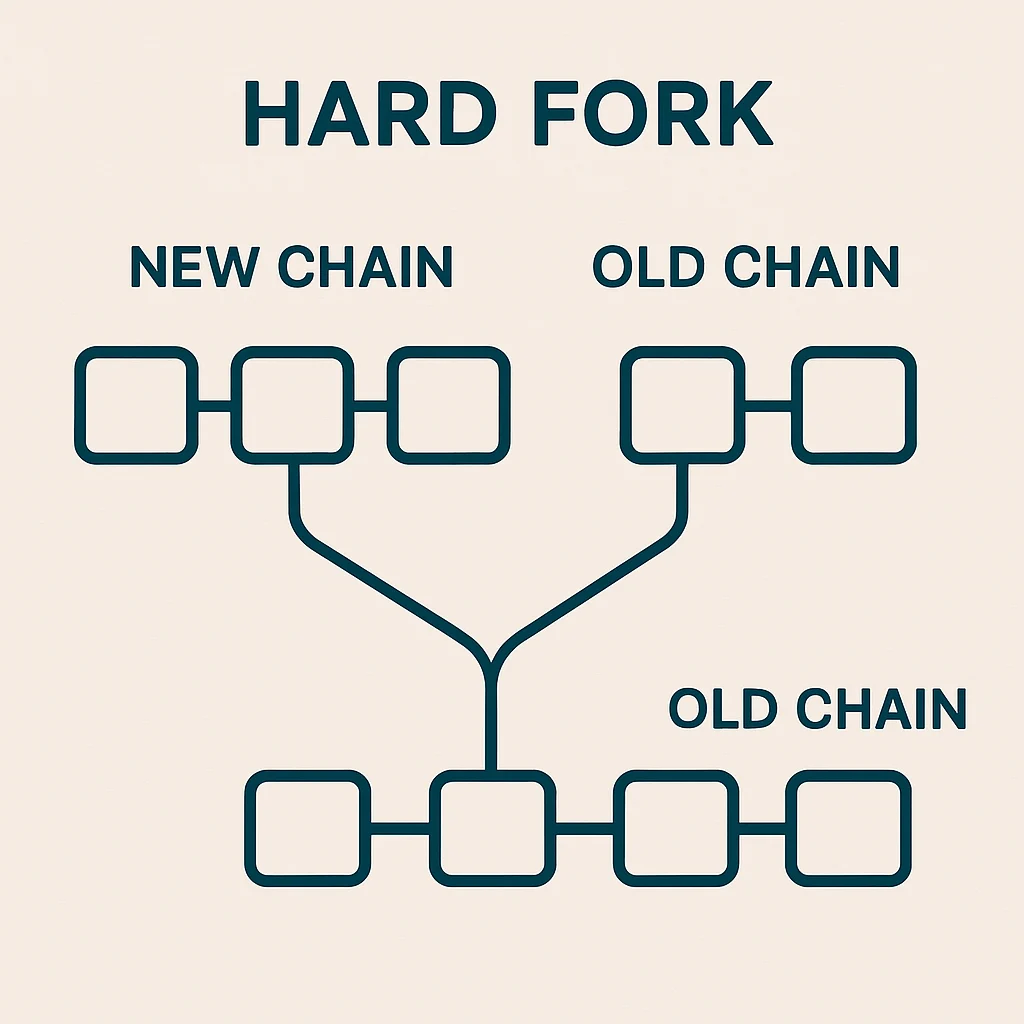
A hard fork is a permanent change to a blockchain’s protocol that makes previously invalid blocks valid, or vice versa, requiring all nodes to upgrade to the new rules. Nodes that don’t upgrade continue following the old chain, potentially creating two separate networks.
How Hard Forks Work
Incompatible changes to blockchain rules require hard forks. This might include changing block size limits, consensus mechanisms, or fundamental protocol features that older software can’t understand.
Network consensus determines which fork becomes the “main” chain. Usually, the fork with more hash power, developer support, and economic activity becomes dominant while the other dies.
Cryptocurrency splits can result when communities disagree about fork changes. Both chains continue operating with their own tokens, exchanges, and user bases.
Real-World Examples
- Bitcoin Cash fork – Disagreement over block size led to permanent split creating BCH
- Ethereum Classic – Original Ethereum chain after the DAO hack hard fork
- Bitcoin SV – Further split from Bitcoin Cash over technical and philosophical differences
Why Beginners Should Care
Free coins sometimes result from hard forks when you automatically receive tokens on both chains. However, this isn’t guaranteed and requires proper wallet management.
Network disruption during contentious hard forks can cause transaction delays, exchange suspensions, and price volatility as markets figure out which chain has value.
Research required to understand which fork to support, as community splits can be permanent and choosing wrong can mean holding worthless tokens.
Related Terms: Soft Fork, Consensus Mechanism, Node, Chain Split
