Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake (PoS): Energy-Efficient Consensus
Proof of Stake secures blockchain networks through economic staking rather than energy-intensive mining. It’s like replacing a gold rush with a security deposit system.
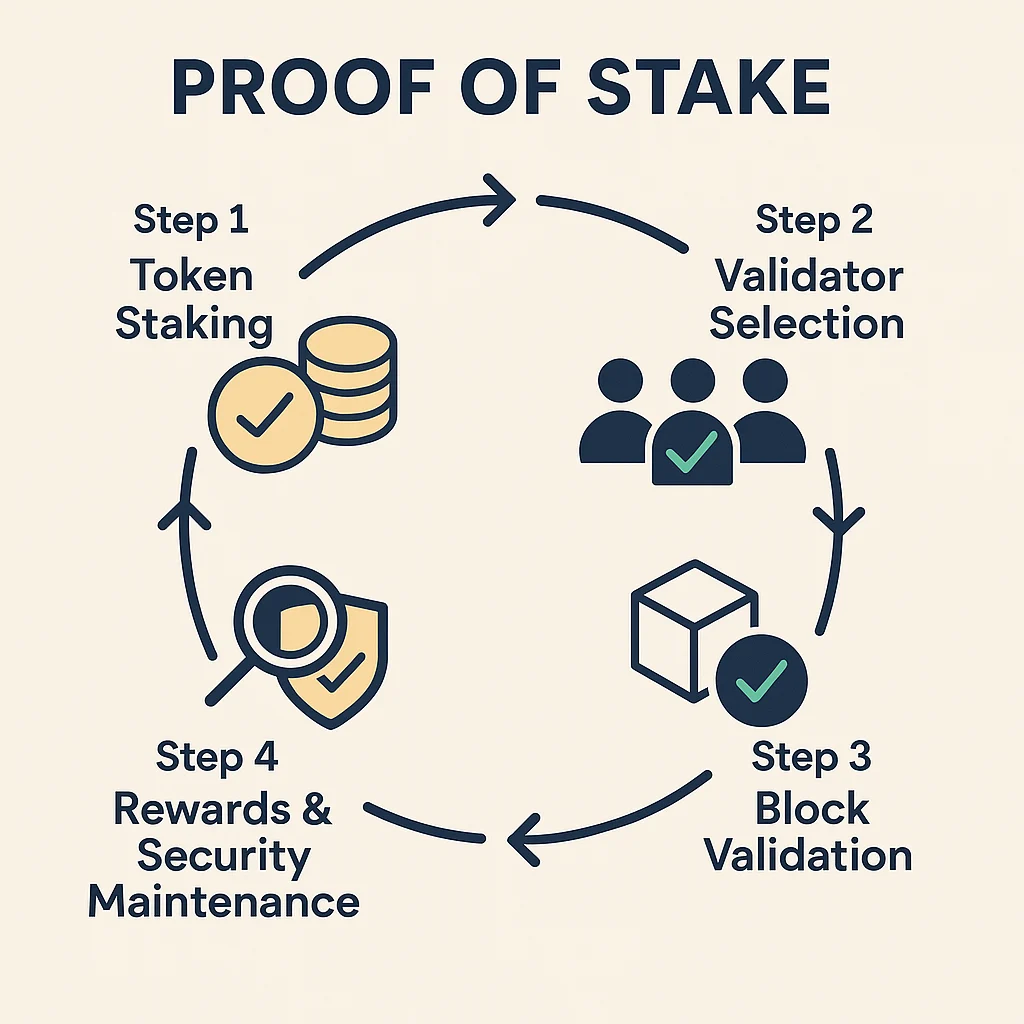
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism where validators are chosen to create new blocks based on their stake in the network rather than computational power. Validators put up cryptocurrency as collateral and earn rewards for honest participation.
How Proof of Stake Works
Stake-based selection chooses validators to propose and validate blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they’ve locked up as collateral.
Economic security aligns validator incentives through rewards for honest behavior and penalties (slashing) for malicious actions or poor performance.
Energy efficiency eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining since validators are selected through economic mechanisms rather than computational competition.
Real-World Examples
- Ethereum 2.0 transitioned from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake in 2022, reducing energy consumption by 99%+
- Cardano built on Proof of Stake from launch with focus on peer-reviewed development
- Polkadot uses nominated Proof of Stake with delegation to professional validators
Why Beginners Should Care
Environmental benefits make PoS networks much more sustainable than energy-intensive Proof of Work mining.
Participation opportunities allow token holders to earn staking rewards by helping secure networks without specialized mining hardware.
Different trade-offs compared to Proof of Work in terms of decentralization, security assumptions, and wealth concentration dynamics.
Related Terms: Staking, Validator, Slashing, Proof of Work
