Staking
Staking: Earning Rewards by Holding Crypto
Staking turns your crypto into a money-making machine. Hold tokens, earn more tokens – it’s that simple. But the devil’s in the details.
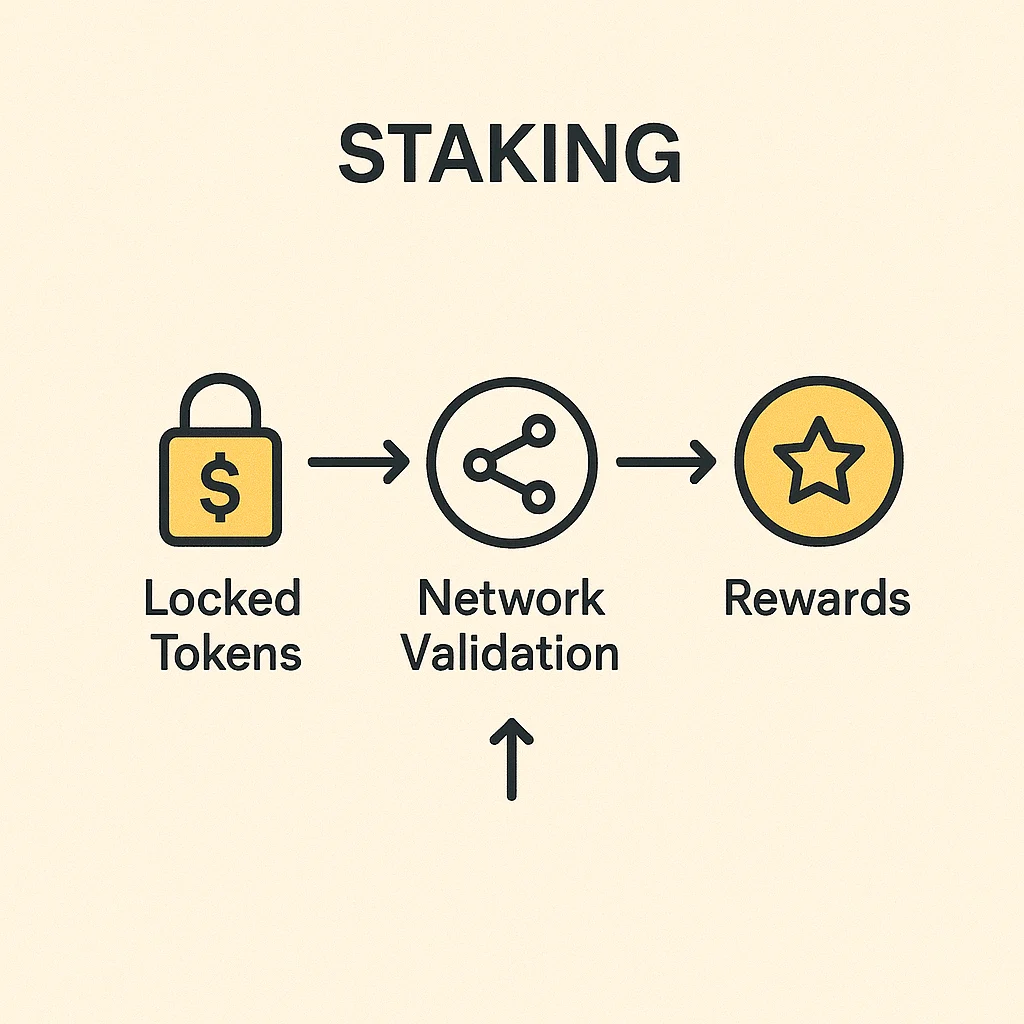
Staking is the process of locking up cryptocurrency tokens to support a blockchain network’s operations and earning rewards in return. Think of it as earning interest on your crypto savings account, except the “bank” is a decentralized network.
How Staking Works
Proof-of-Stake blockchains use staking instead of energy-intensive mining. Token holders lock up their coins as collateral to validate transactions and secure the network.
The network randomly selects validators to create new blocks based on their stake size. Bigger stakes mean more chances to be chosen and earn rewards.
Staking rewards come from transaction fees and newly minted tokens. Annual yields typically range from 5-20% depending on the network and how many people are staking.
Real-World Examples
- Ethereum 2.0 – Stake 32 ETH to run a validator node, earn ~5% annually
- Cardano (ADA) – Delegate stake to pools, earn ~4-6% with no lockup period
- Solana (SOL) – Stake with validators for ~6-8% rewards
Why Beginners Should Care
Staking lets your crypto work for you instead of sitting idle. It’s generally safer than yield farming because you’re supporting established networks rather than experimental protocols.
Some platforms offer liquid staking, giving you tokens representing your staked position that you can trade or use in DeFi while still earning staking rewards.
Related Terms: Proof of Stake, Validator, Yield Farming, Liquid Staking
