Consensus Mechanism
Consensus Mechanism: How Networks Agree
Consensus mechanisms solve the fundamental problem of getting thousands of independent computers to agree on a single version of truth without central authority.
A consensus mechanism is the process by which a distributed network of nodes agrees on the validity of transactions and the current state of the blockchain. It ensures all participants have the same version of the ledger without needing to trust each other.
How Consensus Mechanisms Work
Byzantine Fault Tolerance addresses the challenge of reaching agreement when some network participants might be malicious or unreliable. Consensus protocols must work even with bad actors present.
Economic incentives encourage honest behavior through rewards for following protocol rules and penalties for attempting to cheat or attack the network.
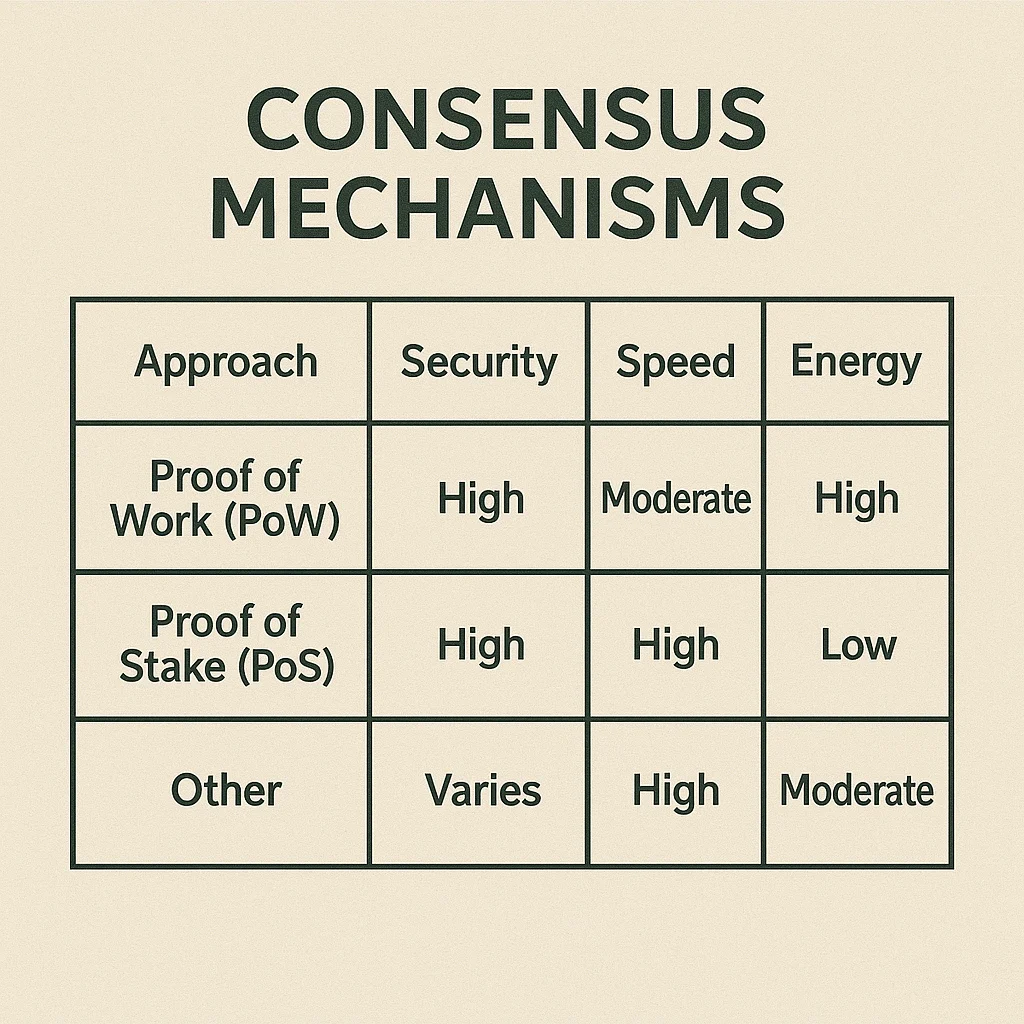
Different approaches trade off between security, speed, and energy consumption. No consensus mechanism is perfect – each makes compromises based on network priorities.
Real-World Examples
- Proof of Work – Bitcoin’s energy-intensive but proven secure consensus mechanism
- Proof of Stake – Ethereum’s switch to more energy-efficient validation through economic staking
- Delegated Proof of Stake – EOS and other networks using representative validation systems
Why Beginners Should Care
Consensus choice fundamentally affects a blockchain’s security, decentralization, and environmental impact. Understanding these trade-offs helps evaluate different cryptocurrency projects.
Network security depends on consensus mechanism design and adoption. Newer or experimental consensus methods may have undiscovered vulnerabilities.
Energy debates often center on consensus mechanisms, with Proof of Work consuming significant electricity while alternatives use far less energy but have different security assumptions.
Related Terms: Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, Validator, Mining
